Question
Question: A voltmeter has a resistance of \(100{\text{ }}\Omega \) . What will be its reading when it is conne...
A voltmeter has a resistance of 100 Ω . What will be its reading when it is connected across a cell of e.m.f of 2 V and internal resistance of 20 Ω
Solution
In order to solve the question, we will first off all will use the ohm’s law to find the current then we will use the relation between EMF, potential difference, internal resistance and current and substitute the value of all given data and current so as to find the potential difference which is the reading of voltmeter.
Formula used:
Ohm’s law
I=RV
V=E−Ir
V refers to potential difference
E refers to EMF
I refer to current
r refers to resistance
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given basic circuit of resistance, battery and internal resistance and we have to find the reading of voltmeter when the internal difference and EMF is added to circuit
Voltmeter is the device used to measure potential difference in the circuit
Resistance (R) = 100 Ω
Internal resistance (r) = 20 Ω
EMF = 2 V
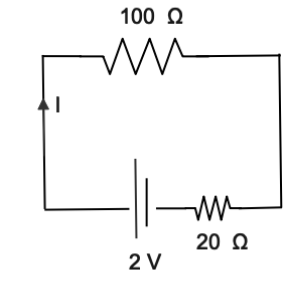
first of all we will use the ohm’s law to find the current
I=RTV
RT is the sum of both the internal resistance and resistance
Now substituting the value
I=100 Ω+20 Ω2V
Calculating for current we get
I=601A
Now we will use the relation between EMF, potential difference, internal resistance and current
V=E−Ir
Substituting the values
V=2−(601)×20
⇒2−0.333
Solving for potential difference we get
V=1.667 V
Hence the reading of voltmeter is 1.667 V
Note: Many of the people may be confused between potential difference and EMF of a cell but the potential difference is the EMF when product of current and the internal resistance is subtracted from the EMF so the EMF will always be greater than potential difference. And voltmeter is always connected in parallel so its presence does not affect the circuit.
