Question
Question: A vertical tower stands on a declivity which is inclined at \({15^ \circ }\) to the horizon. From th...
A vertical tower stands on a declivity which is inclined at 15∘ to the horizon. From the foot of the tower, a man ascends the declivity for 80 feet and then finds that the tower subtends at an angle of 30∘. Find the height of the tower.
Solution
One side of the triangle is given that is 80 feet and the subtended angle form by the tower is 30∘. Since the inclined angle is 15∘, the second angle of a triangle can be found by 90∘−15∘, and the third angle is 180∘−(30+75) .
There are two angles and one side is known.
∴ apply the sine rule in the triangle. The Sine Rule can be applied in any triangle where one side and its opposite angle are known.
Here, use the Sine formula,
⇒ SinAa=SinBb
⇒ Sin75∘80=Sin30∘b
Here, b is the height of the tower.
Complete answer:
Consider the vertical height of the tower is AB. The declivity is the downward slope inclined at 15∘ to the horizon.
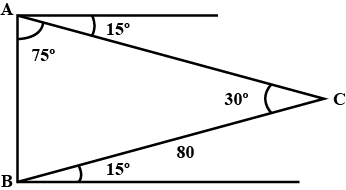
From the above figure the side BC of the triangle ABC is 80 feet and the tower subtends an angle C is 30∘ .
∴∠BCA=30∘
Here, vertical pole AB is making 90∘ with the horizon.
Find the angle ∠ABC ,
⇒ ∠ABC=90∘−15∘
⇒ ∠ABC=75∘
The sum of the angles of the triangle is 180∘. In the triangleABC,
⇒ ∠A+∠B+∠C=180∘
Substitute, ∠B=75∘,∠C=30∘ into the formula and find ∠A,
⇒ ∠A+75∘+30∘=180∘
⇒ ∠A+105∘=180∘
Simplify the equation by subtracting 105∘ from each side of the equation,
⇒ ∠A=180∘−105∘
⇒ ∠A=75∘
Apply the Sine rule of the triangle,
If a, b and c are the sides of the triangle and their corresponding opposite angles are A , B and C then,
⇒ SinAa=SinBb=SinCc
Substitute, a=80∘, A=75∘ and C=30∘ into the Sine Rule,
⇒ SinAa=SinCc
⇒ Sin75∘80=Sin30∘c
Here, c=AB and, it is the height of the tower.
⇒ Sin75∘80=Sin30∘c
⇒ c=Sin75∘80×Sin30∘
Write the angle 75∘ as the sum of 45∘ and 30∘.
⇒ c=sin(45∘+30∘)80×sin30∘…(1)
First solve, sin(45∘+30∘) by using the trigonometric addition formula of sine ;
⇒ sin(A+B)=sinAcosB+cosAsinB
Substitute A=45∘ and B=30∘ into the formula,
⇒ sin(45∘+30∘)=sin45∘cos30∘+cos45∘sin30∘
Use the trigonometric values, sin45∘=21 , cos30∘=23, cos45∘=21 and sin30∘=21.
⇒ sin(45∘+30∘)=21×23+21×21
⇒ sin(45∘+30∘)=223+221
⇒ sin(45∘+30∘)=223+1…(2)
Substitute equation (2) into the equation (1) and use sin30∘=21 .
⇒ c=223+180×21
Simplify further calculation,
⇒ c=3+140×22
Rationalize the term by multiplying the numerator and denominator of the right hand side by 3−1.
⇒ c=3+140×22×3−13−1
⇒ c=(3+1)×(3−1)40×22(3−1)
⇒ c=3−140×22(3−1)
⇒ c=240×22(3−1)
⇒ c=40×2(3−1)
Multiply and simplify the calculation,
⇒ c=40×(6−2)
The height of the tower is 40×(6−2)feet.
Note:
If It is asked to find the length of a side, you need to use the version of the Sine Rule where the lengths are on the top:
⇒ SinAa=SinBb
You will only ever need two parts of the Sine Rule formula, not all three.
If It is asked to find the angle of the triangle, you need to use the version of the Sine Rule where the angles are on the top:
⇒ aSinA=bSinB
Here, a is the side opposite to angle A and b is the side opposite to angle B.
