Question
Question: A uniform heavy rod of length L and area of cross section A is hanging from a fixed support. If youn...
A uniform heavy rod of length L and area of cross section A is hanging from a fixed support. If young’s modulus of the rod is is Y, then the increase in the length of the rod is ( ρ is a density of the material of the rod)
(A) 2ρgL2Y
(B) 2YL2ρg
(C) 2ρYL2g
(D) 3YρL2g
Solution
We will calculate strain using Strain=OriginallengthChangeinlength formula and stress using Stress=AreaForce formula. Then using Young's modulus formula which is stress to strain ratio we will calculate elongation in length of the rod.
Complete step by step answer:
__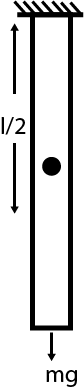
Let us assume the length of rod is L, area of cross section is A and young’s modulus is Y.
Young’s modulus:
It is defined as a tendency of a material to withstand changes made in length when it undergoes compression or expansion.
Change in length of rod =ΔL
Force is acting on the rod in terms of its weight. Elongation takes place when force acts on rod.
Y=StrainStress … (1)
Stress is defined as force per unit area.
Stress=AreaForce
A body of mass ‘m’ is accelerated by ‘a’, object is said to exert a force ‘F’;
Force=mass×acceleration
⇒F=mg … (2)
Strain is defined as the ratio of change in length to its original length.
Strain=Originallength/2Changeinlength=L/2ΔL … (3)
Centre of gravity:
Whole weight of an object is concentrated at the centre.
Y=2AΔLmgL
ΔL=2AYmgL … (4)
Density=VolumeMass
Volume of rod =length×area
ρ=Vm=LAm … (5)
Using equation (4),
ΔL=2AYmgL×LL
Using equation (5),
ΔL=LA×2YmgL
⇒ΔL=2YρgL2
Thus, the length of the rod is increased by 2YL2ρg .
Therefore, option B is correct.
Note: We can solve this question by using Dimensional Analysis in comparing options as well.
The acceleration due to gravity, ‘g’ cannot be taken in the denominator as in Young's modulus formula, stress is taken in the numerator. So, option A is not possible.
Secondly, the center of mass lies at mid-point of the rod instead of one third part of it. So, option D is wrong.
As per formula ρ lies in the numerator. Option B is satisfying this condition. Therefore, it is the correct option.
