Question
Question: A triangle has three vertices A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6). Determine the area of the triang...
A triangle has three vertices A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6). Determine the area of the triangle. Prove that the triangle is a right angle triangle?
Solution
In a 3d space area of triangles or parallelograms can be found by using the cross product of any two adjacent sides. If two vectors are perpendicular they don’t have any kind of projection on each other so their dot product comes to be zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Area triangle in a 3d space can be calculated by taking the half of the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides. And to check whether the triangle is a right-angle triangle or not we need to take the dot product of sides, if any one of the dot products becomes zero then those sides are at right angles to each other and the triangle is a right-angle triangle.
So, here we have a triangle with coordinates as A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6).
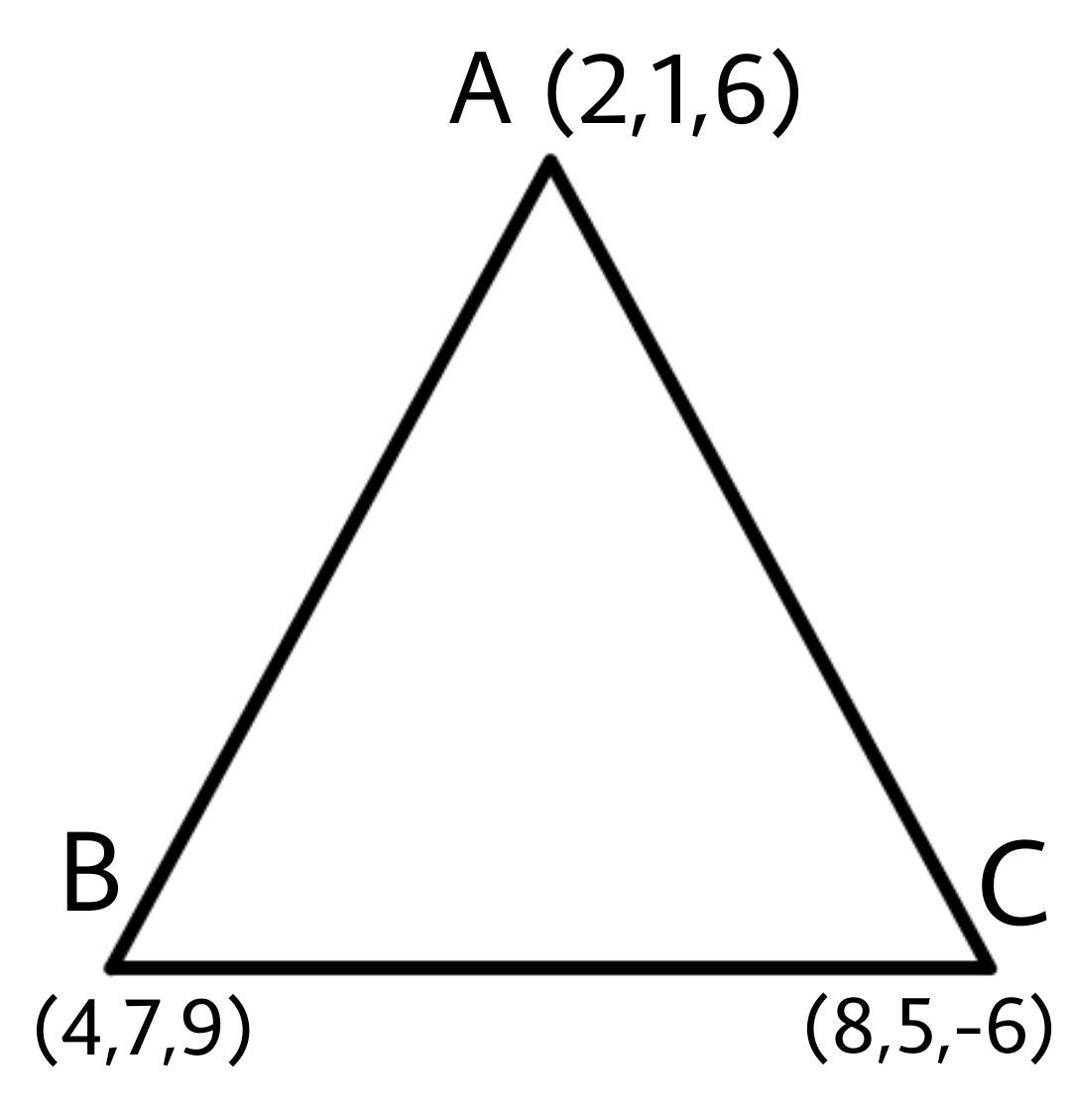
Let’s find the sides this is done by subtracting the coordinates:
For AB we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of B.
AB=(4−2)i+(7−1)j+(9−6)k
AB=2i+6j+3k
For BC we will subtract the coordinates of B from the coordinates of C.
BC=(8−4)i+(5−7)j+(−6−9)k
BC=4i−2j−15k
For AC we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of C.
AC=(8−2)i+(5−1)j+(−6−6)k
AC=6i+4j−12k
Finding the area:
For area we will take the cross product of any two sides, let’s take AB and AC
