Question
Question: A transformer is used to A. convert DC into AC B. convert AC into DC C. obtain the required DC...
A transformer is used to
A. convert DC into AC
B. convert AC into DC
C. obtain the required DC voltage
D. obtain the required AC voltage
Solution
A transformer is a device that increases or decreases the voltage or current of a circuit and gives it as the output. It works on the principle of magnetic induction and Faraday’s law. It only works with ac current.
Formula used:
emf=−Ndtdϕ
Complete answer:
A transformer is a device that can increase or decrease the voltage of the circuit as per requirement. It consists of a primary coil and secondary coil. The primary coil acts as an input and the secondary coil acts as an output.
It can also be used to increase or decrease the current input current.
A transformer works on the principle of magnetic induction. We know that a current induces a magnetic field and a changing magnetic field through a coil produces an emf in the coil.
Therefore, an alternating current is required in the transformer. Which means that a transformer only works with ac source and the output is also AC output.
Hence, a transformer is used to obtain the required AC voltage or current.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
A schematic diagram of a transformer is given below.
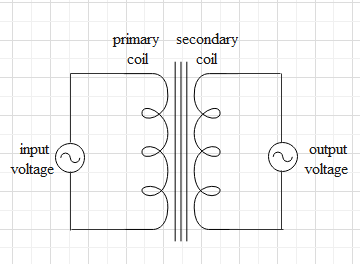
The input (primary coil) of the transformer contains an ac source, which produces an alternating current. Which induces a changing magnetic field through the coil. Therefore, there is a changing flux through the primary coil.
The primary and secondary coils are wounded to a soft iron core as shown in the diagram. The property of this iron core is that it does allow the magnetic field to go out of the core and hence, the magnetic field lines are confined to the core.
As a result, all the magnetic field lines produced due to the AC source in the primary circuit pass through the secondary coil. Hence, a varying flux is generated in the secondary coil.
According to Faraday’s law, a changing flux induces an emf in the coil that is equal to emf=−Ndtdϕ, where N is the number of turns in the coil.
Now let the number of turns in the primary coil be Np and the number of turns in the secondary coil be Ns.
Let the emf of the primary coil be Vp and emf of the secondary coil be Vs.
Therefore,
Vp=−Npdtdϕ and Vs=−Nsdtdϕ
Divide both the equations.
Hence,
VpVs=NpNs=k.
k is called the turn ratio or transformer ratio.
If the number of turns in the primary coil are less than the number of turns in the secondary coil, then the output voltage is more than the input voltage. This type of transformer is called a step-up transformer.
If the number of turns in the primary coil are more than the number of turns in the secondary coil, then the output voltage is less than the input voltage. This type of transformer is called a step-down transformer.
Note:
For an ideal transformer, there is no loss of power. This means that the input power (Pp) is equal to the output power (Ps). i.e. Ps=Pp
We know that Pp=Vpip and Ps=Vsis.
⇒Vsis=Vpip
⇒VpVs=isip
And VpVs=NpNs
Therefore,
isip=NpNs
However, for a real transformer there is power loss and the output power is always less than the input power. The ratio of the output power to the input power is called the efficiency (η) of the transformer. i.e. η=PpPs
⇒η=VpipVsis
