Question
Question: A \[{{\text{C}}_{11}}{{\text{H}}_{16}}\left( {\text{A}} \right)\] reacts with two equivalents of \[{...
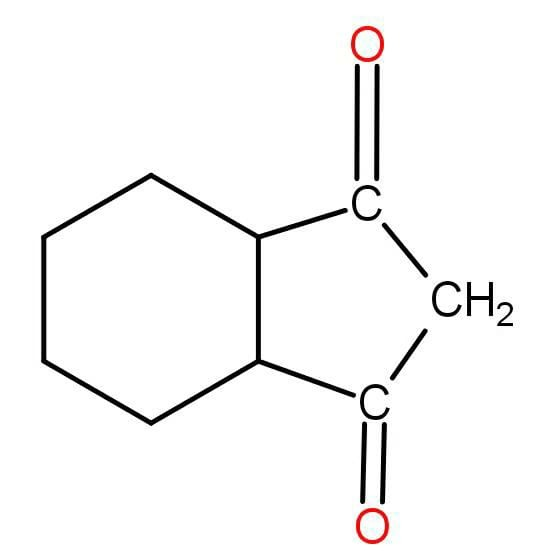
A C11H16(A) reacts with two equivalents of H2 and on reductive ozonolysis gives two equivalents formaldehyde and (B) of following structure.
Identify the structure of (A) .
Solution
We have to proceed in a reverse manner. The product is given to us and we have to find the reactant. Remove the oxygen added to the product B and replace them with carbon we will get the reactant.
Complete answer:
Ozonolysis is a process of addition of oxygen in a double bond. This process leads to the formation of aldehyde or ketone products. As the name suggests the ozonolysis is carried out in the presence of ozono. During reductive ozonolysis the reducing agents are used along with ozone. Zinc and water is used as a reducing agent in reductive ozonolysis.
The statement given that C11H16(A) reacts with 2 equivalents of hydrogen reacts suggests us that the molecule contains 2 double bonds. One molecule of hydrogen gets added up in one double bond each hydrogen atom on each carbon. It is given to us that two molecules of hydrogen are getting consumed so that means two double bonds must be present here.
Now ozonolysis is addition of oxygen instead of double bond. The reverse of ozonolysis will be the removal of the oxygen and placing carbon at their place. So the structure of the compound A will be:
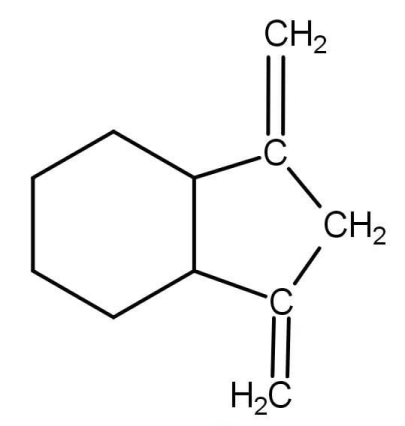
As we can see that it contains two double bonds and will react with 2 equivalents of hydrogen.
Different compounds undergo ozonolysis to yield different compounds.
Note:
The ozonolysis of alkene can give alcohol, aldehyde, ketones and acid. Alkynes also undergo ozonolysis to form anhydrides. The azo compounds also show an ozonolysis reaction and form nitrosamine.
