Question
Question: A tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant. When t...
A tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant. When the F1 plants were selfed the resulting genotypes were in the ratio of
A) 1:2:1::Tall homozygous : Tall heterozygous : Dwarf
B) 1:2:1:: Tall heterozygous : Tall homozygous :: Dwarf
C) 3:1 :: Tall : Dwarf
D) 3:1 :: Dwarf : tall
Solution
In part, pea plants were great choices for the analysis because they have many noticeable features that occur in two distinct ways. Mendel was capable of crossing pea plants with various forms of characteristics by regulating pollination.
Complete answer:
First we should know about Mendel’s experiment to answer this question. For all seven features, Mendel also does the same experiment. In each case, in the F1 plants, one quality of the characteristic vanished and then appeared again in the F2 plants. And even in that case, 75% of F2 plants also had characteristic value and 25% had the other. Mendel developed his first law of inheritance based on these observations. The law of segregation is called this law.
Now, let us find the solution from the options-
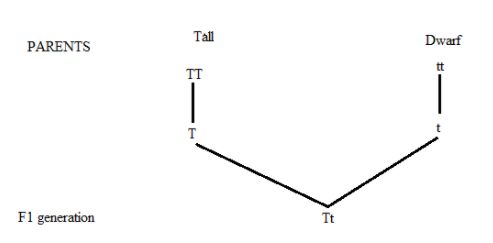
All tall (Tt) plants are formed in F1 progeny by a cross between pure breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) plants. The 50 percent gametes with "T" allele and 50 percent with "t" allele are generated by these heterozygous tall plants.
F2 generation:
| T| t
---|---|---
T| Tt| Tt
t| Tt| tt
The spontaneous fusion of these gametes by two heterozygous tall plants results in a 3:1 combination of tall and dwarf plants. Of the 3/4 tall trees, 1/4 is tall homozygous (TT) and 2/4 is tall heterozygous (Tt). Thus, option B is not the correct option.
3:1 is the genotypic ratio. Thus, option C is not the correct option.
While 1/4 is the dwarf in the F2 generation, 3/4 plants are tall. Thus, option D is not the correct option.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A) 1:2:1:: Tall homozygous: Tall heterozygous : Dwarf
Note: At a time when the blending theory of inheritance was common, Mendel investigated the inheritance of traits in pea plants. That would be the theory that offspring have a mix of their parents' features.