Question
Question: A student observed a permanent slide showing asexual reproduction in yeast. Draw diagrams of the o...
A student observed a permanent slide showing asexual reproduction in yeast.
Draw diagrams of the observations he must have from the slide. Name the process also.
Solution
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which a single parent produces a new progeny. The new individuals produced are genetically and physically similar to one another, implying that they are clones of their parents. Both multicellular and unicellular species exhibit asexual reproduction. There will be no gamete fusion, and the number of chromosomes will not alter as a result of this procedure. It will inherit the same genes as the parent, with the exception of a few circumstances where a rare mutation may occur.
Complete answer:
Asexual reproduction in yeast is called budding.
Budding is the process of creating a person from the buds that grow on the parent body. Hydra is a budding organism that reproduces itself. The parent organism provides nutrients and protection to the bud, which then detaches once fully grown.
Asexual reproduction via budding is the most prevalent mechanism of vegetative growth in yeast, when a tiny bud (also known as a bleb or daughter cell) is generated on the parent cell. The parent cell's nucleus separates into two daughter nuclei, which migrate into the daughter cell. The bud then grows until it separates from the parent cell and forms a new cell. During the budding process, the daughter cell is usually smaller than the mother cell. Some yeasts, such as Schizosaccharomyces pombe , reproduce through fission rather than budding, resulting in two daughter cells of the same size. In general, haploid cells die under high-stress situations like as nutrition deprivation; nevertheless, diploid cells can undergo sporulation, beginning sexual reproduction (meiosis) and creating a variety of haploid spores, which can then mate (conjugate), reconstructing the diploid.
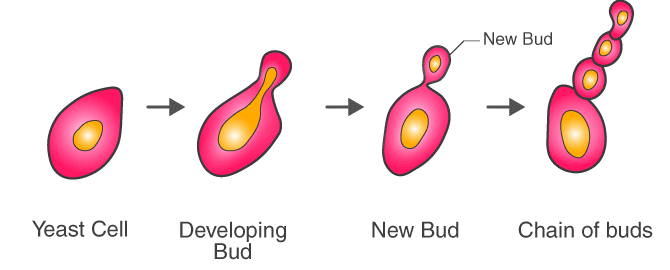
Diagram showing Budding in yeast
Note:
The most prevalent form of fungus that causes yeast infections is Candida albicans. Other kinds of Candida fungus can produce yeast infections that are more difficult to treat and require more aggressive treatments. Candidiasis is a fungus infection caused by the Candida yeast (a type of fungus). Candida albicans is the most prevalent Candida species that can cause infection in humans. Candida can live without causing problems on the skin and inside the body, in places including the mouth, throat, gut, and vaginal canal. “Vitamin D insufficiency is connected with increased autoimmunity and susceptibility to infection”, according to a 2011 study by Cynthia Aranow, M.D. Vitamin D deficiency was also discovered in people with Candida , yeast, bacterial overgrowth, and a variety of digestive problems.
