Question
Question: A student is standing at a distance of 50 meter behind a bus. As soon as the bus starts with an acce...
A student is standing at a distance of 50 meter behind a bus. As soon as the bus starts with an acceleration of 1m/s2. The student starts running towards the bus with a uniform velocity u. Assuming the motion to be along straight road the minimum value of u, so that the student is able to catch the bus is
A. 5ms−1
B. 8ms−1
C. 10ms−1
D. 12ms−1
Solution
In this problem acceleration and initial velocity is given. So first calculate the distance travelled by student with the help of Newton's II equation. We will get this distance in terms of time ‘t’. Now, according to the given situation we make an equation in terms of time ‘t’ and velocity ‘u’ and on solving this. Equation we will get the minimum value of velocity ‘u’ to catch the bus. Newton’s II equation is given as:
S=ut+21at2
Where, s= displacement travelled by particle ,u= initial velocity ,a= acceleration and t= time.
Complete step by step answer:
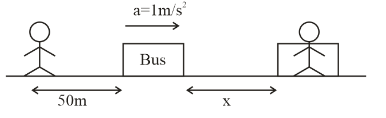
Let the distance traveled by bus be x. When the student caught is after time t.
So, according to newton’s II equation.
S=ut+21at2
For bus, given that
Initial velocity of bus u=0
Acceleration of bus a=1m/s2
So x=0+21×1×t2
x=2t2 …..(1)
Let the velocity of student is u. and given that acceleration of student a=0.
So, the distance traveled by the student is-
S=ut+21at2
⇒s=ut …..(2)
So from diagram it is clear that
s=x+50
From equation 1 and 2
ut=2t2+50
⇒t2+50=2ut
⇒t2−2ut+100=0 …..(3)
Above relation must have real roots.
So,
b2−4ac⩾0
From equation 3
b=2u
⇒a=1
⇒c=100
So,
(24)2−4×1×100⩾0
⇒4u2−400⩾0
⇒4u2⩾400
⇒u2⩾4400
⇒u2⩾100
∴u⩾10
Hence the minimum velocity of the student must be 10 m per sec.
So, option C is the correct answer.
Note: In many problems if a particle is not moving along a straight road. If it is moving in 2 dimensions then Newton's equation is applicable in 2 directions separately i.e. in x-direction and y-direction both.When the object travels in a straight line, irrespective of the direction is known as one-dimensional motion. When the object travels in x and y coordinates with a constant velocity, it is known as two-dimensional motion.
