Question
Question: A storage battery is connected to a charger for charging with a voltage of 12.5V.The internal resist...
A storage battery is connected to a charger for charging with a voltage of 12.5V.The internal resistance of the storage battery is 1. When the charging current is 0.5 A , the emf of the storage battery is
A ) 13V
B) 12.5V
C) 12V
D) 11.5 V
Solution
Kirchoff’s voltage rule(KVL): In an current loop of an electrical network the algebraic sum of emfs is equal to the algebraic sum of the products of currents and resistances in different parts of that loop.
∑E=∑IR Where E is emf and R is resistance and I is current
Complete step by step answer:
Given data :
Internal resistance(r) =1.
Charging current (I) = 0.5A
Source voltage(V) = 12.5V ( since charging source doesn’t have the internal resistance voltage and emf of source are same)
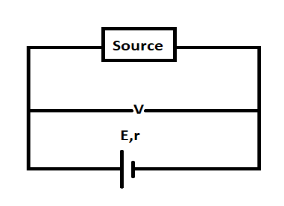
Here E and r is the emf and internal resistance of the storage battery , V is the voltage of the source(no internal resistance for source)
Now applying the KVL for the above current loop
Now applying the KVL for the above current loop
Current from the source going anticlockwise and encounters a positive terminal of the . storage battery, hence E in LHS is taken negative
V−E=Ir
Rearranging the terms and substituting for E of the storage battery
E=V−Ir
Putting the values of V ,I, r in the equation
E=12.5−(0.5)1
E=12V
hence the emf of storage battery is 12V, correct option is C
Note: Always remember that Kirchhoff's voltage law(KVL) is based on conservation of energy. When the circuit has many components( resistors and batteries) it is convenient to use KVL rather than ohm’s law.
