Question
Question: A stone of 1kg is thrown with a velocity of 20 m/s across the frozen surface of a lake and comes to ...
A stone of 1kg is thrown with a velocity of 20 m/s across the frozen surface of a lake and comes to rest after travelling a distance of 50m. What is the force of friction between the stone and the ice?
Solution
Hint: The frictional force acting on the stone balances the force propelling the stone forward when the stone comes to rest. By using the equations of motion and the known values we can calculate the magnitude of frictional force.
Detailed step by step solution:
We are given a stone whose mass is given as
m=1kg
It is thrown across the surface of a frozen lake with a velocity given as
u=20m/s
As the stone slides across the surface of lake, the ice exerts a frictional force, denoted by f, on the stone due to which the stone loses its energy and eventually comes to rest after travelling a distance of
S=50m
Now we can draw a free body diagram for stone and ice in the following way:
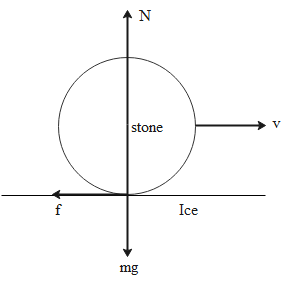
Now we see that as the stone comes to rest, it is due to the frictional force f which balances the force with which the stone is propelled forward. Therefore, we can say that
f−ma=0 ∴f=ma
Now we can use the equation of motion given as
v2−u2=2aS
Now since the stone comes to rest, the final velocity v = 0. Therefore we can calculate the value of acceleration of stone by using the known values in above equation as follows:
u2+2aS=0 ⇒(20)2+2a(50)=0 ⇒100a=−400 ⇒a=−4m/s2
Hence, the magnitude of frictional force is given as follows:
f=ma=1×(−4)=−4N
This is the required answer to the question.
Note: The frictional force always acts in the direction opposite to the direction of motion of the body. The negative sign for frictional force means that the force is acting in the opposite direction and deceleration is taking place in the motion of the stone when it slides over the surface of the lake.
