Question
Question: A stone is projected from the ground with velocity 50 m/s at an angle of 30° It crosses a wall after...
A stone is projected from the ground with velocity 50 m/s at an angle of 30° It crosses a wall after 3 sec. How far beyond the wall the stone will strike the ground? (g = 10 m/s2)
Solution
As the body is projected at an angle, it will be a projectile motion and then we can find the time of flight for complete motion, then for the required distance, time will be the difference between the total and crossing the wall.
Velocity vectors will be usinθ and ucosθrespectively for x and y axes.
Formula used:
s=ut+21at2, where s is displacement, u is initial velocity, a is acceleration and t is time
speed=timedistance
Complete step by step answer:
As the stone is projected at an angle θ of 30°, it will be in a projectile motion
The time of flight of this projectile will tell after how much time it will come to rest.
Using Newton’s laws of motion:
s=ut+21at2
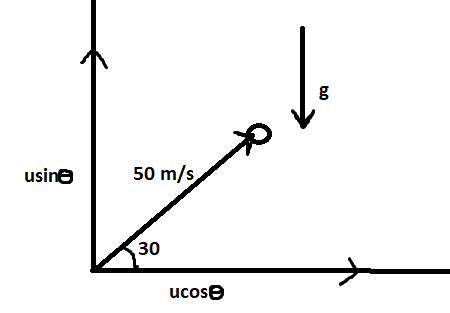
The motion of this projectile is in y – direction so the quantities with respect to that are:
Displacement (s) = 0 [displacement is only along x – axis]
Initial velocity (u) = usinθ [along y - axis]
Acceleration (a) = g [since in air acceleration is only due to gravitational force
Time (t) = T [time of flight]
⇒0=usinθT+21gT2
⟹2usinθ=gT ⇒T=g2usinθ
For the given projected stone:
Angle (θ) = 30°
Initial speed (u) = 50 m/s [given]
Calculating its time of flight:
T=102×50sin30(∵g=10) ⟹T=102×50×21(∵sin30=21) ⟹T=5
Thus, in 5 seconds the stone will come to rest.
It is given that it crosses the wall in 3 seconds.
The time left before it touch the ground is:
t = (5 – 3) seconds
t = 2 seconds.
The distance it will cover beyond wall will be along x – axis
Using the formula:
speed=timedistance distance=speed×time
Speed = ucosθ [along x – axis]
Time = 2s [remaining time]
\Rightarrow dis\tan ce = u\cos 30 \times 2\left( {\because \theta = {{30}^o}} \right) \\\
distance= 50× 23 ×2 ∵θ = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} \\\
distance=503m
Therefore, the distance the stone covers beyond the wall is 503m or 86.6 m.
Note:
When a body is thrown at an angle in air, it is known as projectile, its motion is called projectile motion and its path is called trajectory
When the object is in air, it is only under the force of gravity acting at all its position downward in direction, due to this reason, always a parabolic path is covered.
