Question
Question: A steady current \[I\] goes through a wire loop PQR having a shape of right angle triangle with PQ=3...
A steady current I goes through a wire loop PQR having a shape of right angle triangle with PQ=3x, PR=4x and QR=5x. If the magnitude of magnetic field at P due to this loop is k(48πxμ0I). Find the value of k.
A. 9
B. 5
C. 10
D. 7
Solution
Determine the values of the altitude of the right angle triangle and the distances of the hypotenuse divided by the altitude. Determine the values of sine of angles made by the altitude from a vertex of the triangle with the other two sides of the right angle triangle. Substitute these values in the formula for magnetic field for a right angel triangle.
Formulae used:
The area of a triangle is
Area of triangle=21×base×height …… (1)
The area of a right angled triangle is
Area of triangle=21×altitude×hypotenuse …… (2)
The magnetic field at a point P on the vertex of the right angle triangle is given by
The area of a triangle is
B=4π(altitude of triangle)μ0I(sinθ1+sinθ2) …… (3)
Here, is the permeability of free space, is the current and are the angles made by the altitude of the triangle from one of the vertices with the two sides of the right angle triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that a steady current I goes through a wire loop PQR having a shape of right angle triangle with PQ=3x, PR=4x and QR=5x. Let us first draw the diagram for the wire loop POR.
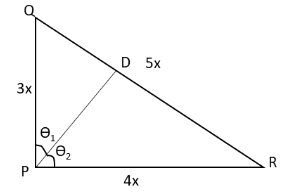
In the above diagram, PD is the altitude of the right angled triangle. The angle made by the altitude of this triangle with the sides PQ and PR of the right angle triangle are θ1 and θ2 respectively.
The area of the triangle PQR is given by using equations (1) and (2).
Area of triangle=21×PR×PQ
Substitute 4x for PR and 3x for PQ in the above equation.
Area of triangle=21×4x×3x
⇒Area of triangle=6x2
And
Area of triangle=21×PD×QR
Substitute 5x for QR in the above equation.
Area of triangle=21×PD×5x
Equate these two areas of the triangles.
21×PD×5x=6x2
⇒PD=512x
Now we can determine the length of QD using Pythagoras theorem.
PQ2=PD2+QD2
Substitute 3x for PQ and 512x for PD in the above equation.
(3x)2=(512x)2+QD2
⇒QD2=9x2−25144x2
⇒QD=59x
The length of the side QR is the sum of the lengths QD and DR.
QR=QD+DR
Substitute 5x for QR and 59x for QD in the above equation.
5x=59x+DR
⇒DR=516x
The sine of an angle in a right angle triangle is the ratio of the side opposite to that of the angle and hypotenuse.
Hence, the value of angles sinθ1 and sinθ2 is
sinθ1=PQQD
⇒sinθ1=3x59x
⇒sinθ1=159
And
sinθ2=PRDR
⇒sinθ2=4x516x
⇒sinθ2=2016
Let us determine the value of the magnetic field.
Substitute PD for altitude of triangle in equation (3).
B=4π(PD)μ0I(sinθ1+sinθ2)
Substitute 512x for PD, 159 for sinθ1 and 2016 for sinθ2 in the above equation.
B=4π(512x)μ0I(159+2016)
⇒B=48πx5μ0I(300180+240)
⇒B=48πxμ0I(60420)
∴B=7(48πxμ0I)
From the above equation, we can conclude that the value of k is 7.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note: The same question can be solved by another method. If one considers the angles made by the remaining angles of the right angle triangle other than the right angle then the formula for magnetic field used will be the same. The only thing we need to change is to take the cosine of these angels instead of sine of the angles.
