Question
Question: A stationary particle explodes into two particles of masses \({{m}_{1}}\) and \({{m}_{2}}\) which mo...
A stationary particle explodes into two particles of masses m1 and m2 which move in opposite direction with velocities v1 and v2. The ratio of the kinetic energiesE2E1 is
A. m2m1B. 1C. m2v1m1v2D. m1m2
Solution
- Hint: First we will learn about Newton's third law. It states that for every action in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction. In other words, if object A exerts a force on object B, then object B also exerts an equal and opposite force on object A.
Complete step-by-step solution -
In the question it is given that the particle is stationary initially. Momentum of a particle is defined as the mass of the particle times its velocity. The particle’s initial velocity is 0. Hence, momentum will be zero. The explosion of the particle follows conservation of linear momentum principle. This states that, since no external force is acting on the particle, the momentum of the particle remains constant.
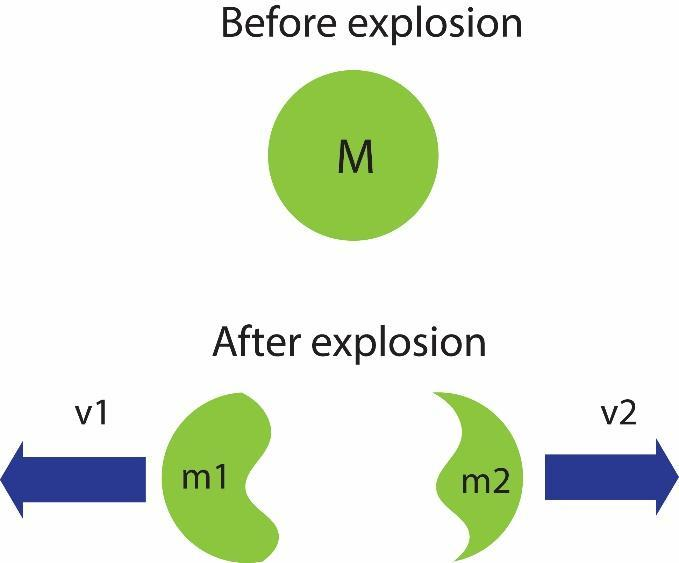
This means, after explosion, the total momentum is zero. The total momentum after explosion is given by,
m1v1=m2v2 . Here, the negative symbol is because the masses travel in opposite directions after the explosion. From, conservation of momentum, we can conclude that,
