Question
Question: A solution of (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small a...
A solution of (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of a small amount of SbCl5, due to the formation of:
A. Carbene
B. Carbocation
C. Free radical
D. Carbanion
Solution
For this problem, we have to write the complete reaction in which firstly the antimony pentachloride will remove the chlorine atom from the given compound. Due to which the formation of the intermediate will take place.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given question, we have to determine the correct intermediate which will be formed when (-) - 2-chloro-2-phenylethane in toluene will react with antimony pentachloride.
- As we know that the toluene is the 6-membered ring structure on which one methyl group is also attached.
- Now, when antimony pentafluoride reacts with the 2 - chloro - 2 - phenylethane which is present in the solution of toluene, it removes the chlorine molecule which is attached with the carbon atom as shown below:
Cl - CH(Ph) - CH3 SbCl5Toluene Ph - CH+ - CH3 + SbCl6−
- Here, the carbocation formed is known to have planar geometry.
- Also, the central carbon atom is known as chiral carbon because it is attached to the four different groups that are chlorine, phenyl, hydrogen and methyl group.
- Now, when an electrophile attaches to the carbocation then it will form two types of the compound and forms a racemic mixture.
- The attack of the electrophile take place from two places that are upward and lower as shown below
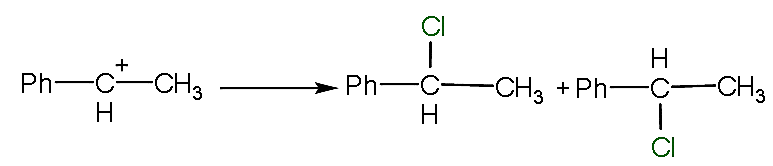
- Here, the mixture is known as d and l mixture which is also known as a racemic mixture.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: As free radical is the unpaired pair of electrons whereas carbanion is the carbon species which consist of a negative charge or electrons. In carbene, the carbon molecule consists of two valence electrons and two unshared electrons.
