Question
Question: A solution contains 1 millicurie of L-phenylalanine \[^{{\mathbf{14}}}{\mathbf{C}}\](uniformly label...
A solution contains 1 millicurie of L-phenylalanine 14C(uniformly labelled) in 2.0 mL solution. The specific activity of the labelled sample is given as 150 millicuries/mmol. The activity of the solution in terms of counting per minute/mL at a counting efficiency of 80% is :
A. 88.8×107cpm/L
B. 88.8×106cpm/mL
C. 88.8×105cpm/mL
D. 88.8×107cpm/mL
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of the specific activity of a labelled sample. The specific activity can be defined as the activity per quantity of a radionuclide and it is a physical property of that radionuclide.
Formula used: molarity=V (in mL)moles (in mmol)
Complete Step by step solution:
To answer this question let us first calculate the concentration of the given labelled sample.
(a) 1 mmole = 150 millicurie, using unitary method
1 millicurie=1501 mmol
Now, concentration can be calculated by dividing the moles with the given volume
molarity=V (in mL)moles (in mmol)=150×21=3.33×10−3M
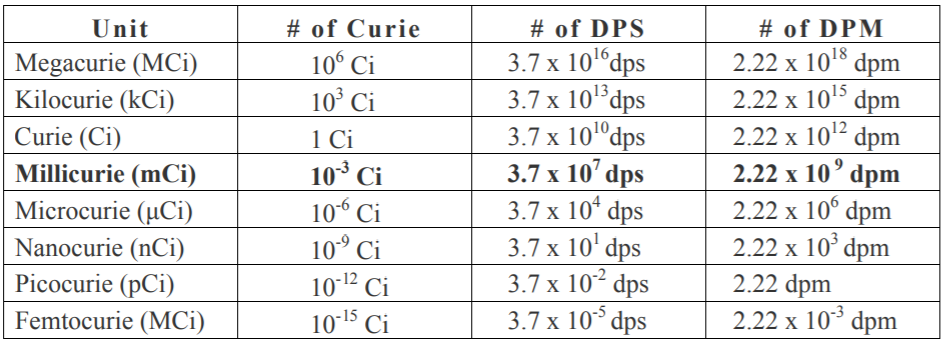
b) We know that 1 curie = 3.7×1010dps= 3.7×1010×60 dpm . This can be converted to counting per minute:
⇒3.7×1010×60×10080 counting per minute
∴ 1 millicurie = 3.7×1010×60×10080×10−3cpm.
To achieve the final answer we need to divide this value with volume.
⇒3.7×1010×60×10080×10−3×21
⇒88.8×107cpm/mL
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is option D.
Additional information: The emissions in most of the spontaneous radioactive decays involve alpha (α)particle, the beta (β) particle, the gamma-ray, and the neutrino. The alpha particle is the nucleus of doubly charged He24. Beta particles can be beta minus beta plus. Beta minus is an electron created in the nucleus during beta decay. Beta plus particle is also known as a positron, is the antiparticle of the electron; when brought together, two such particles will mutually annihilate each other.
Note: To answer the questions related to radioactivity you need to know the important conversion units regarding the disintegration of a radioactive compound.