Question
Question: A solid sphere of uniform density and radius R applies a gravitational force of attraction equal to ...
A solid sphere of uniform density and radius R applies a gravitational force of attraction equal to F1 on a particle placed at P, distance 2R from the centre O of the sphere. A spherical cavity of radius R/2 is now made in the sphere as shown in figure. The sphere with cavity now applies a gravitational force F2 on the same particle placed at P. The ratio of F2/F1 will be
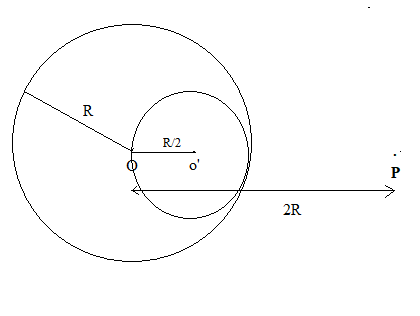
A. 1/2
B. 7/9
C. 3
D. 7
Solution
First of all, we will see what is gravitational force and its expression. We will solve this question using superposition principle. For the original sphere, we will calculate the gravitational force F1 on particle P and to calculate F2, we will subtract the gravitational force due to the sphere of radius R/2 from F1.
Complete answer:
The magnitude of the gravitational force that two particles of masses m1and m2separated by a distance r exert on each other is F=Gr2m1m2 .
Here ‘G’ is gravitational constant and its value is 6.67×10−11Nm2/kg2.
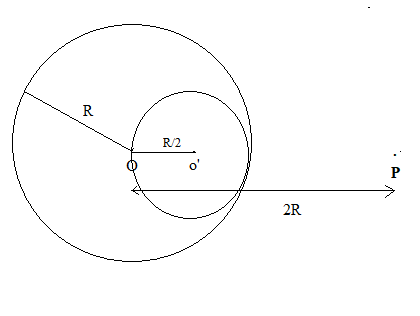
Let the mass of the sphere with radius R be M kg.
For density to be constant:
v1M1=v2M2 (1)
Using the above equation, we will calculate the mass of the sphere with radius R/2.
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
34πR3M=34π(2R)3M2
⇒M2=8M kg
Now, we will calculate the force F1.
Here r = 2R.
m1= M kg
∴F1=Gr2m1m2=G(2R)2Mm2=G4R2Mm2 = Gravitational force due to sphere of radius R.
= F1 - Gravitational force due to sphere of radius R/2.
=G4R2Mm2−G(23R)28Mm2=36R27GMm2
Therefore, F1F2=4R2GMm236R27GMm2=97.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
Newton was the first to propose a force law for gravitation, which is stated as follow:
Every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This force is called gravitational force.
Note:
In this type of question, you remember the formula for finding gravitational force. It should not be confused with ‘G’ and ‘g’. ‘G’ is a universal constant whereas ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity of earth. The direction of gravitational force is along the line joining the particles.
