Question
Question: A small block of mass 1kg is released from rest at the top of a rough track. The track is a circular...
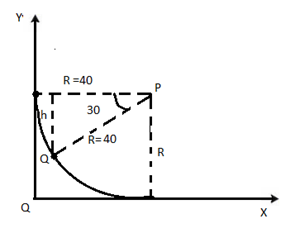
A small block of mass 1kg is released from rest at the top of a rough track. The track is a circular arc of radius 40m. The block slides along the track without toppling and a frictional force acts on it in the direction opposite to the instantaneous velocity. The work done in overcoming the friction up to the point Q, as shown in the figure below, is 150J. (Take the acceleration due to gravity, g=10m/s2. The speed of the block when it reaches the point Q is
A)5m/s
B)10m/s
C)103m/s
D)20m/s
Solution
Since the block is at a height it possesses potential energy. When it is released, it starts losing potential energy. This energy is converted into the kinetic energy. But here, some energy is used against the friction. The initial potential energy of the block is equal to the sum of kinetic energy at point Q and the work done against the friction.
Formula used:
mgh - Work done against friction =21mv2
Complete answer:
Since the block is resting at a height, it possesses some potential energy. When the block is released and reaches the point Q after falling through a height h, it loses its gravitational potential energy. Out of this 150Jis used against the friction. Hence, the remaining energy is transferred as the kinetic energy21mv2, where v is the velocity at point Q. Then,
Potential energy - Work done against friction =Kinetic energy
mgh - Work done against friction =21mv2
Where,
m is the mass of block
g is the acceleration due to gravity
h is the height
v is the velocity of block
Therefore,
mgh−150=21mv2--------- 1
Given that,
Mass, m=1Kg
g=10m/s
Given that, the radius of the circle is 40m. Then, from figure,
h=Rsin30∘=2R
Then,
h=40×Sin 30=20m
Substitute the values of m, g and hin equation 1. We get,
1×10×20−150=21×1×v2
v=10m/s
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Every system obeys the conservation of energy in the absence of friction or friction is negligible. If we consider a system that experiences only conservative forces, there is a potential energy associated with each force, and the energy only changes form between kinetic energy and various types of potential energy, with the total energy remaining constant.
