Question
Question: A shower of rain appears to fall vertically downwards with a velocity 4km/h on a person walking west...
A shower of rain appears to fall vertically downwards with a velocity 4km/h on a person walking westwards with a velocity of 3km/h. The actual velocity and direction of the rain is
A. 1km/h, clockwise to vertical
B. 5km/h, anticlockwise to vertical
C. 5km/h/h, clockwise vertical
D. 1km/h, vertically downwards
Solution
Velocity of rain with respect to the man VRM is given as 4km/h.Therefore on substituting the value of velocity of rain with respect to the man and velocity of man with respect to the ground RM we get the velocity of rain with respect to the ground that is the actual velocity of the rain VR.
Complete step by step answer:
Given the relative velocity of rain with respect to the man VRM=−4j^.
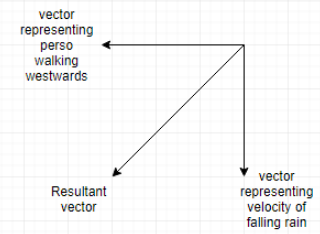
The velocity of man with respect to the ground VM=−3i^. To find the actual velocity of rain that is the velocity of rain with respect to ground we substitute the given value in the following equation VRM=VR−VM.
Therefore the actual velocity of rain is VR=VRM+VM.
VR=(−4)j^+(−3)i^
Magnitude of VR,
VR=(−3)2+(−4)2 ⇒VR=9+16 ⇒VR=25 ∴VR=5km/h
Its direction is in the 4th quadrant i.e. clockwise to vertical.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Relative velocity is always written with respect to a reference. Relative velocity of the first object with respect to the second object is the difference of the actual velocity of the first object and the actual velocity of the second object. The direction of motion can be determined with the help of a vector. Relative Velocity is the velocity of an object relative to some other object which might be stationary, moving slowly, moving with same velocity, moving with higher velocity or moving in the opposite direction.
