Question
Question: A short linear object, of length l, lies along the axis of a concave mirror, of focal length f, at a...
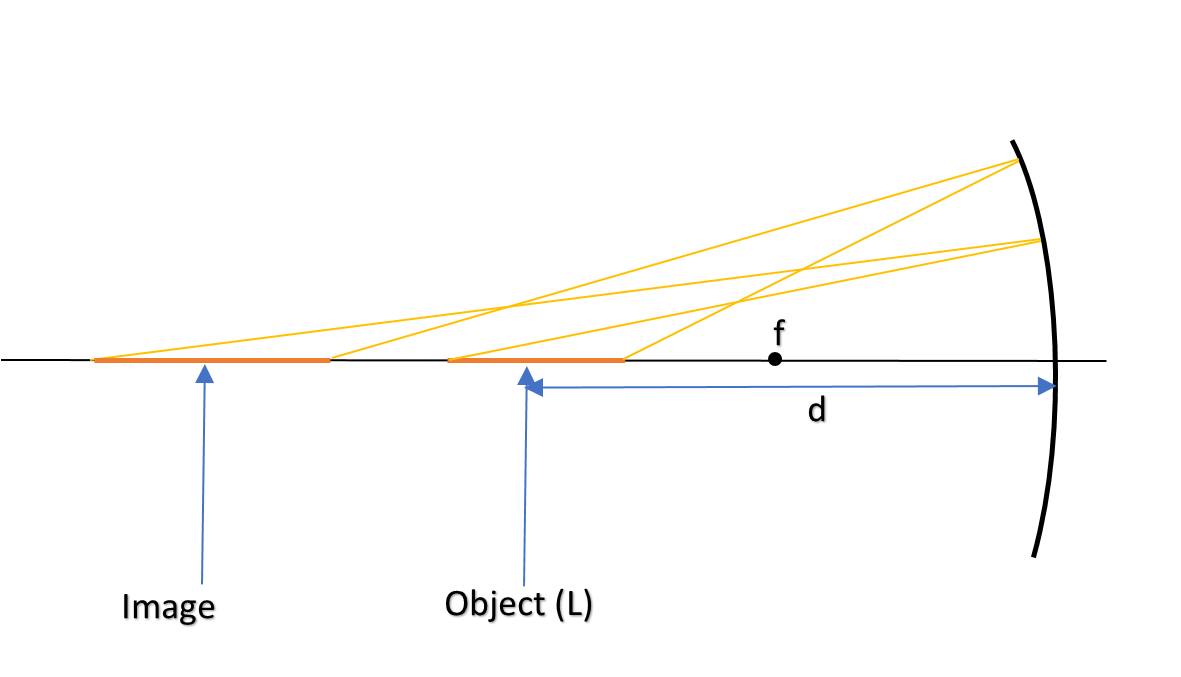
A short linear object, of length l, lies along the axis of a concave mirror, of focal length f, at a distance ‘d’ from the pole of the mirror. The size of the image is then (nearly):
A.d−ffl
B.fld−f
C.f2(d−f)2l
D.(d−f)2f2l
Solution
As the object is short, we can assume the distance of one end of the object approximately equal to the distance of the other end of the object. Hence we can use differentiation in solving this type of problems.
Formula used:
f1=u1+v1
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all, we shall find the image distance.
Putting the values of f and u with proper sign conventions, we get;
−f1=−d1+v1
⟹v=f−ddf
Differentiating the mirror formula, we get
d[f1=u1+v1]
⟹0=u2−1du−v21dv
Now, as per our assumption, du=l and dv = size of image.
Putting the values in the equation:
⟹0=u2−1du−v21dv
⟹0=d2−1du−(f−ddf)21dv
⟹dv=(f−df)2×du
As du=l, thus;
⟹dv=(f−df)2×l
Or dv=(f−d)2f2l
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information: Magnification of a device is the ability to produce an enlarged image of the object placed in front of it. Hence, mathematically it is the ratio of size of image to the size of the object. A concave mirror can be used to produce both enlarged and diminished images of any object. Also it could be used to produce both real and virtual images of the object.
Note: Here, a negative sign shows that the object is placed to the left of the mirror. Students should practice image formation by different mirrors in several cases. Concave mirror is very useful in many cases. It could be used as a reflector or as a heater. It can form real as well as virtual images of an object. It can also produce enlarged as well as diminished image of an object. Students are highly advised to learn how to use sign conventions in optics problems. Avoiding which could result in the wrong answer every time.
