Question
Question: A sample of 2kg Helium (assumed ideal) is taken through the process ABC and another sample of 2kg of...
A sample of 2kg Helium (assumed ideal) is taken through the process ABC and another sample of 2kg of the same gas is taken through the process ADC, then the temperature of the states A and B is:
Given: R =8.3joule/mol K
A.TA = 120.5K, TB = 120.5K
B.TA = 241K, TB = 241K
C.TA = 120.5K, TB = 241K
D.TA = 241K, TB = 120.5K
Solution
Volume and pressure for both the samples of Helium can be calculated from the diagram. No. of moles can be calculated by dividing the mass in grams with the molar mass of helium and R is a constant which will be the same in both the cases. Solve individual reactions separately to the value of temperature.
Formula used:
PV = nRT
Where P is pressure, V is volume, n is number of moles, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature.
Number of moles, n = molar mass of substance (in gmol - 1)mass of substance (in grams)
Complete step by step answer:
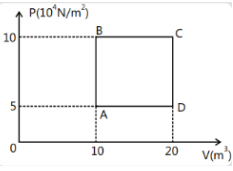
We need to calculate the value of temperature at stage A and B with the given parameters. On the x axis of the graph volume in m3 has been plotted and on y axis pressure in 104N/m2 has been plotted. What this means is we have to multiply the value we get on the y axis with 104 to get the actual value of pressure.
So this is a P - V curve. The coordinates of points will give us the value of volume and pressure.
Let us first do it for stage A. If we look at the diagram point A cuts x axis at point 10 that means the volume of gas at point A will be VA = 10 m3 and it cut y axis at point 5, so the pressure at stage A will be PA=5×104 m3. Mass of helium is 2kg or 2000g and the molar mass of helium is 4 gmol1.
