Question
Question: A ring of radius \(R\) is placed such that it lies in a vertical plane. The ring is fixed, A bead of...
A ring of radius R is placed such that it lies in a vertical plane. The ring is fixed, A bead of mass m is constrained to move along the ring without any friction. One end of the spring is connected with the mass m and the other end is rigidly fixed with the topmost point of the ring. Initially the spring is in an un-extended position and the bead is at a vertical distance R from the lowermost point of the ring. The bead is now released from rest.
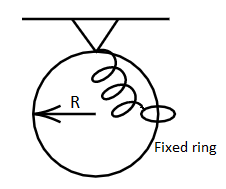
a) What should be the value of spring constant K such that the bead is just able to reach the bottom of the ring.
b) The tangential and centripetal accelerations of the bead at initial and bottommost position for the same value of spring constant K.
Solution
Spring constant K can be derived with the help of the formula of Hooke’s law. The spring constant K,represents how stiff the spring is. Stiffer the springs the higher the spring constants. The displacement of an object is a distance measurement that describes that change from the normal, or equilibrium, position.
Formula used:
F=−Kx
Where,
F denotes the force, K denotes the spring constant, x denotes the distance the spring is stretched or compressed from its rest position.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that,
Radius of the ring R ,
Mass of the bead m ,
Vertical distance R ,
(a) Once the bead reaches the bottom of the ring it will have zero velocity. According to Hooke’s law to find the spring’s constant we can use Newton’s second law motion;
The natural length of the spring is 2R
F=−Kx
By using Newton’s second law motion;
Kx=mg
Where,
mdenotes the mass of the bead,
g denotes the gravity due to acceleration.
Since x=(2R−2R) ,substitute the value;
⇒K(2R−2R)=mg
since we only need the spring constant K ;
⇒K=2R(2−1)mg
⇒K=32Rmg(2+1)
(b) initially, when the bead is at the A , there is no spring force acting on it. Therefore, centripetal acceleration initially is zero.
That is initially Centripetal acceleration =0 ;
Tangential acceleration;
α=Iτ
Where,
αdenotes the tangential acceleration,
τ denotes the torque,
I denotes the moment of inertia.
Since we know;
Torque τ=mgR
Moment of inertia I=mR2
Where,
m denotes the mass of the bead,
g denotes the gravity due to acceleration.
R denotes the radius of the ring.
Therefore, substitute the values of torque and moment of inertia,
At the point A the torque is due to gravity;
⇒α=mR2mgR
Simplifying the equation by cancelling the like terms;
⇒α=Rg
At the point B the bead just reaches. Therefore, the centripetal acceleration is zero, since at this point no tangential forces are acting on it, the tangential acceleration is also zero.
Therefore, (a) spring constant K=32Rmg(2+1).
(b) at point A ;
⇒ Tangential acceleration α=Rg
⇒ Centripetal acceleration =0
At point B ;
⇒ Tangential acceleration =0
⇒ Centripetal acceleration =0
Note: The tangential acceleration is not constant, it may change when the radius of the ring or the mass of the bead. The S.I. unit of spring constant K is N/m, the S.I. of tangential acceleration is m/s2 and the S.I unit of centripetal acceleration is also m/s2.
