Question
Question: A ring is made of a wire having a resistance \({R_0} = 12\Omega \). Find the points A and B as shown...
A ring is made of a wire having a resistance R0=12Ω. Find the points A and B as shown in figure, at which a current carrying conductor should be connected, so that the resistance R of the sub circuit between these points is equal to 38Ω
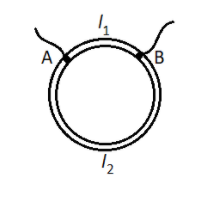
A) l2l1=85
B) l2l1=31
C) l2l1=83
D) l2l1=21
Solution
In order to find the ration between the in-between lengths of the circuit, remember the resistance of the conductor is proportional to the length of that conductor. When we take resistance between two points in a wire ring we consider the ring as two different sub circuits which are in parallel connection.
Complete step by step solution: Let’s define all the data given in the question.
The resistance of the wire used to make the ring, R0=12Ω
Resistance of the sub circuit between the points A and B, R=38Ω
We are asked to find out the ratio between the two lengths that formed in between the two points A and B as shown in the figure.
We know the resistance of a wire, R=Aρl
Where, ρ is the resistivity of the wire
l is the length of the wire
A is the cross-sectional area of the wire
In this case the same wire is used for both lengths, so the resistivity and the cross sectional area of the wire will be the same for both lengths.
So, the resistance will be proportional to the length of the wire.
That is, R∝l
When we consider the whole ring as two sub circuits between the two points A and B, we can see that these two circuits are in a parallel connection.
Let R1 be the resistance of length l1
And R2 be the resistance of length l2
∴R1+R2=R0=12Ω …………………………………….. (1)
In a parallel connection, we know,
⇒R11+R21=83
⇒R1R2R1+R2=83
Applying the value from equation (1), we get,
⇒R1R212=83
⇒R1R24=81
⇒R1R2=32
We know, (a+b)2=a2+b2=2ab
⇒(R1+R2)2=R12+R22+2R1R2
⇒122=R12+R22+2×32
⇒144−64=R12+R22
∴80=R12+R22
Solving this equation we get two values for R1 and R2, 4 and 8
We choose R1=4 and R2=8 according to the options given, so,
∴ R2R1=l2l1=84=21
The correct option is (D), l2l1=21.
Note: The term resistance is a measure of how difficult it is to transmit current through a wire. The term resistivity is a characteristic of the material used in a wire or any electrical component, whereas the resistance is a characteristic of the electrical component or wire. Resistance of a wire depends on the resistivity of the material used.
