Question
Question: A resistor of resistance R is connected to a cell of internal resistance \(5\Omega \). The value of ...
A resistor of resistance R is connected to a cell of internal resistance 5Ω. The value of R is varied from 1Ω to 5Ω. The power consumed by R is
A) Increases continuously
B) Decreases continuously
C) First decreases then increases
D) First increases then decreases
Solution
The resistance is connected in every circuit to control the flow of current in the circuit. Because the heavy flow of current leads to the breakdown of the circuit. Hence we can say that the resistance offers the resistive force against the current flow. And the voltage is provided by the cell in some circuits. While transferring the voltage to the circuit, the cell develops heat in it. This heat is due to the heavy flow of the voltage supply. To avoid this heavy flow of voltage, the cell itself develops a resistance called internal resistance.
Formula used:
We know that power is the product of voltage and current. Therefore, power,
P=V×I
P=I2R
∴P=R2V2R
Where,
V=voltage
R=resistance
Complete step by step answer:
(i) If the voltage is provided by the cell, it experiences the resistance called internal resistance. This is due to the heat produced in the battery. Hence the resistance in the circuit is R+r.
(ii) The equation for the power we derived is P=R2V2R
(iii) We have to calculate the power consumed by R and the circuit has an additional resistance called internal resistance. Hence the equation is converted in to
P=(R+r)2V2R
(iii) The resistance R is direct to power. Hence R increases, the power consumed by R also increases.
(iv) Therefore we can say that when the resistance R is varied from 1Ω to 5Ω, the power consumed by R also increases continuously.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
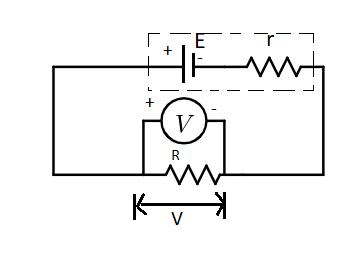
(i) The internal resistance is the resistance offered by the cell providing EMF. This is due to the heat produced in the cell. If the voltage provided by the cell is e. Then e=I(R+r). The R is the resistance provided by the resistance.
(ii) From the previous equation, e=IR+Ir. We know that V=IR. Hence the equation becomes, e=V+Ir
(iii) From this equation, we can say that the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
(iv) The internal resistance is also measured in Ohms.
Note:
The internal resistance is the additional resistance developed in the circuit. If the internal resistance in the circuit is more, then the current flowing through the circuit will decrease and the power also decreases. And in turn, if the internal resistance is small, the current in the circuit increases, and power also increases. And the voltage developed in the cell is greater than the voltage across the terminals.
