Question
Question: A ray of light is travelling in a glass cube placed in water. Find the critical angle for the glass-...
A ray of light is travelling in a glass cube placed in water. Find the critical angle for the glass-water interface (n = 1.5 for glass and n = 1.33 for water).
A.sin−1(0.8867)
B.cos−1(0.7867)
C.sin−1(0.7867)
D.cos−1(0.8867)
Solution
Critical angle – It is an angle on which if light is incident from denser to rarer medium, it won’t go outside the medium but will refract through 90∘. After this angle, the light will come back in the same medium as if the mirror is placed in its path. This phenomenon is called total internal reflection, also known as TIR.
Formula used: critical angle(c)=sin−1[n1n2]
Complete answer:
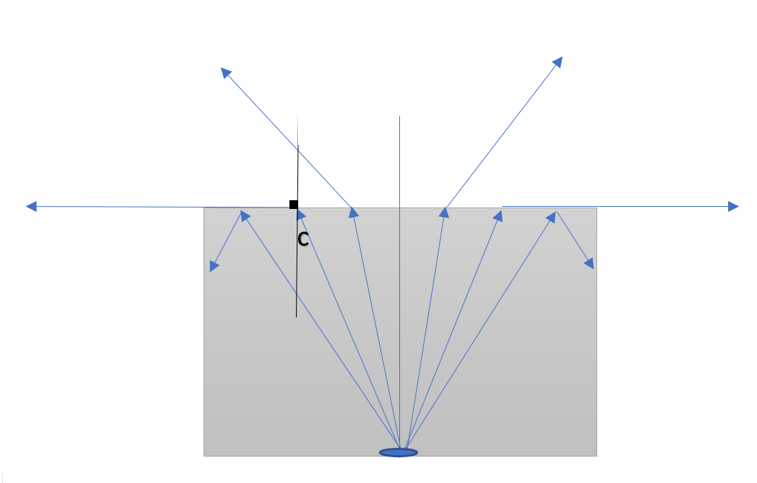
In the above figure shown, the slab is placed inside water and a source of light is placed at the bottom of the slab which emits radiation in all directions. For the medium, we are given n2=1.33 (in which rays are going) and n1=1.5 (from which rays are coming). The critical angle is shown in the figure by ‘c’.
To calculate the critical angle, we will use:
critical angle(c)=sin−1[n1n2]
c=sin−1[1.51.33]≈sin−1(0.8867)=62.45∘
Thus, option A. is correct.
Additional information:
The critical angle depends upon both the mediums from which rays are coming and in which rays are going. When the medium in which rays are going is air or vacuum, the critical angle becomes critical angle(c)=sin−1[μ1].
Note: The speed of light changes if it enters from one medium to another. Refractive index is a property of the medium which is the measure of how slow the speed of light gets on entering a medium. The refractive index is a unique property of a medium which can be constant or variable. Certain physical quantities like temperature govern the change of refractive index of a material. These concepts of total internal reflection (TIR) and critical angle are very important in understanding different natural phenomena like the formation of a rainbow is based on the concept of total internal reflection.
