Question
Question: A ray of light, incident on an equilateral prism \(({\mu _g} = \sqrt 3 )\) moves parallel to the bas...
A ray of light, incident on an equilateral prism (μg=3) moves parallel to the baseline of the prism inside it. Find the angle of incidence for this ray.
Solution
Use the concept of planar geometry and then find out the angle of reflection. After that use Snell’s law to find out the angle of incidence.
Complete step by step solution:
The above situation can be visualized as
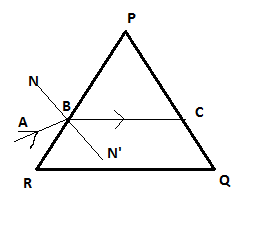
Here the NN′ is the normal. Since the prism is an equilateral prism, therefore each angle including the angle of prism A is equal to 60∘
∴A=60∘
Now we use some geometry here
∠BRQ=60∘ since it is an equilateral prism
∴∠RBC=120∘ Since RQ∣∣BC given in question
∠N′BR=90∘ Since NN′ is the normal
Using above data we get that
∠N′BC=∠RBC−∠N′BR
Substituting the values in the above equation we get;
∠N′BC=120∘−90∘
∠N′BC=30∘ Which is the angle of refraction.
Now using snell's law,
μ1sini=μ2sinr
Substituting the values in the above equation we get;
⇒1×sini=3sin30∘
Calculating further we get;
⇒sini=23
⇒i=sin−123
∴=60∘
Therefore the angle of incidence i=60∘.
Additional Information:
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The traditional geometrical shape of an optical prism is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism" usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prisms are not in fact in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, plastic, and fluorite. Prism is generally used to split white light into its constituent colours.
Note: Use Snell’s law appropriately. Questions of these types require good knowledge of planar geometry. Hence one should be sound in knowledge of planar geometry. Read about all other terms and properties of prism.
