Question
Question: A ray of light incident at an angle \[\theta \] on a refracting face of prism emerges from the other...
A ray of light incident at an angle θ on a refracting face of prism emerges from the other face normally. If the angle of prism is 5∘ and the prism is made of material of refractive index 1.5 , the angle of incidence is:
A. 7.5∘
B. 5∘
C. 15∘
D. 2.5∘
Solution
First of all, we will find out the angle of refraction on the first face, by applying a formula which relates angle of prism and angles of refraction. Then we will use Snell’s law, followed by substitution of required values. We will manipulate accordingly and obtain the result.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given problem, we are supplied with the following data:
Angle of the prism is given as A=5∘ .
Refractive index μ=1.5 .
We are asked to find out the angle of incidence on the face of the prism.
To begin with, we need to draw a diagram of the prism shown by the incident rays and the refracted rays, for a better understanding.
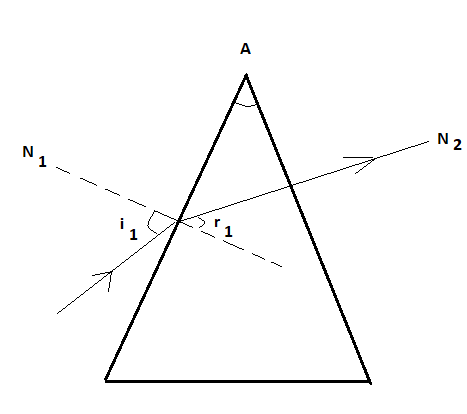
From the diagram, it is quite clear that the incident ray and the refracted ray on the other face of the prism are lying on the normal itself. There is no phenomenon of refraction on the other face because the incident ray hit the other face in perpendicular direction, so we can write:
Angle of incidence on the other face is i2=0∘ .
Angle of refraction on the other face r2=0∘ .
We know:
r1+r2=A r1=A−r2 r1=5−0 r1=5∘Again, by Snell’s law, we have that the ratio of sine of angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is always a constant and it is the basic property of that medium. It is called the refractive index of that medium.
μ=sinr1sini1 sini1=μsinr1 ⇒sini1=1.5×sin5∘ ⇒sini1=1.5×0.087Again, by simplifying further, we get:
⇒sini1=0.1305 ⇒i1=sin−1(0.1305) ⇒i1=7.5∘Hence, the angle of incidence on the face of the prism is 7.5∘ . The correct answer is option A.
Note: It is important to note that you have seen that the light ray emerges from the prism at right angle, so it is quite obvious that the light ray had not suffered refraction. The light ray is undeviating in nature. So, remember that in this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction on the other face are both zero.
