Question
Question: A ray gets successively reflection from two mirrors inclined at an angle of \[{40^o}\]. If the angle...
A ray gets successively reflection from two mirrors inclined at an angle of 40o. If the angle of incidence for the first mirror is 30o, then net deviation of this ray after two reflections:
A) 40o
B) 280o
C) 180o
D) 240o
Solution
We can easily solve the question by using laws of reflection. We know that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Also, we can use the relation between the angle deviation and the angle of incidence. using these two relations we can easily find the answer to the given question.
Complete step-By-Step Answer:
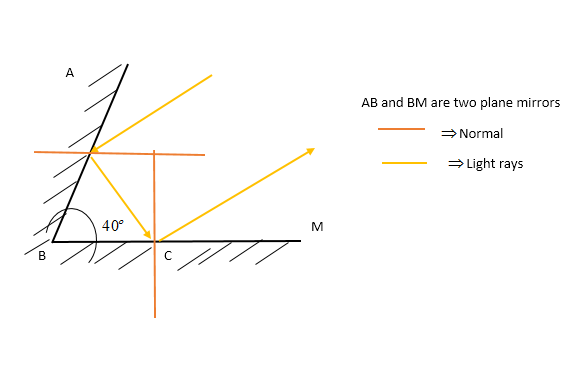
It is given in the question that:
The angle between the two mirrors =40o
The angle of incidence on the first mirror =30o
We know the laws of reflection states that when a light is reflected off a surface, angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
Let ∠i be the angle of incidence and∠r be the angle of reflection.
Thus, ∠i=∠r
The angle of reflection in the first mirror =30o
Thus, angle of deviation denoted by δ1 is =π−2×∠i
⇒180o−60o
δ1=120o
We also know, from the laws of reflection, the angle of reflection, the angle of incidence and the normal together sums up to180o.
The normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
Now, considering triangle ABC in the diagram:
∠BAC=90o−30o=60oSince the normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
∠ABC=40o(GIVEN)
Using the angle sum property we, obtain:
∠ACB=80o
Normal of the second mirror also makes right angle with the plane of the mirror, thus, ∠ACD=90o−80o=10o
This is the angle of incidence and it equals angle of reflection for the second mirror.
Thus angle of deviation in mirror 2 is given by:
δ2=π−2i2
Where, i2 represents the angle of incidence for the second mirror.
δ2=180o−20o=160o
Therefore, total angle of deviation is given by:
δ=δ1+δ2
⇒δ=120o+160o=280o
This is our required solution.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Angle of deviation, as we know, is defined as the angle between the straight line path and the reflected ray, which is equal to twice the angle of deviation.
Image formed by the plane mirror is virtual, erect and of the same size as that of the object.
