Question
Question: A pyramid has a square base of side a, and four faces which are equilateral triangles. A charge Q is...
A pyramid has a square base of side a, and four faces which are equilateral triangles. A charge Q is placed on the centre of the base of the pyramid. What is the net flux of electric field emerging from one of the triangular faces of the pyramid?
a) 0
b) 8ϵoQ
c) 8ϵoQa2
d) 2ϵoQ
Solution
If charge is not at symmetry so, first adjust the charge so that it is at identical distance from all faces. So, that the electric lines passed through all the faces should be equal in number, after that electric flux will be easy to calculate.
Complete answer:
It is given that there is a pyramid with a square base and a charge Q is placed on the center of the base i.e., center of the square. So, charge is placed in an unsymmetrical figure, to make it symmetrical we consider a similar pyramid attached to it. After attaching a pyramid Now it is a symmetrical figure i.e., symmetrical Octahedron.
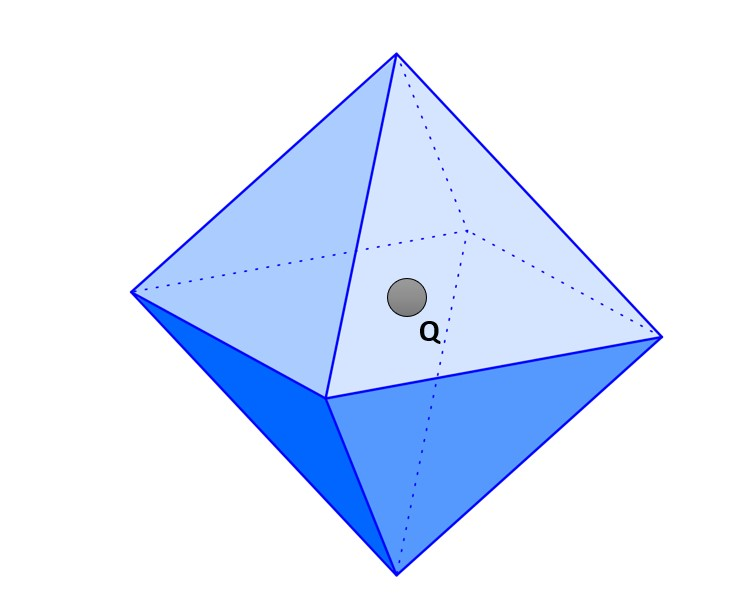
When there is charge Q in a closed body then flux through it will be-
ϵoQ.
Now flux through the symmetrical octahedron is
ϵoQ.
Now there are triangular faces and flux through each face will be equal as now it is a symmetrical system.
So, flux through a single face is 81th times of total flux.
ϕ=8ϵoQ
So, option (b) is correct.
Additional Information:
Electric flux is defined as the number of electric field lines passing through a given area and it is totally depending on the charge. If there is no charge enclosed so electric field lines will be zero passing through the closed surface. Also, flux will be zero.
Note:
- Flux is due to the charge enclosed and it is also equal to the dot product of Electric field and the area through which lines passed. Also noted that Electric fields can be affected by the charges outside the closed surface but outside charges will not affect the electric flux.
