Question
Question: A projectile of mass \(m\) is fired with velocity \(v\) from a point as shown in figure, neglecting ...
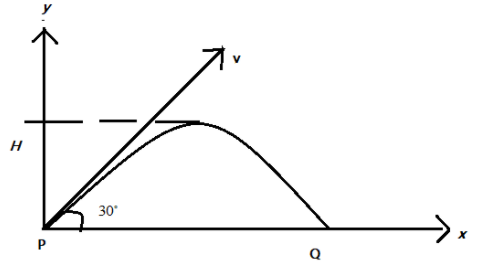
A projectile of mass m is fired with velocity v from a point as shown in figure, neglecting air resistance, what is the change in momentum when leaving P and arriving at Q?
Solution
A body experiences a projectile motion when the object is projected at an inclination from the ground. Then the body follows a curved path, which is parabolic in nature and is called the ballistic trajectory. Then the distance covered by the body along the x and y-axis respectively is given as, R and H which is the maximum horizontal range and maximum height attained by the object.
Formula:
mΔv=mu−mv
Complete answer:
We know that momentum p is a quantity which describes the state of the object. It is given as p=mv where m is the mass of the object and v is the velocity of the object.
We know that projectile motion has two components, namely the x and y components
Then, we can express the components of velocity v as vcos30 along the x-axis and vsin30 along the y-axis.
Now to find the change in momentum along PQ, we can ignore the horizontal constant as it remains the same throughout the along PQ. Then clearly, as PQ is along the vertical component, there is change in momentum along the vertical direction.
Then the change in momentum is given as, mΔv=mu−mv . Here, the final velocity is the negative of the initial velocity. Then we get, mΔv=mvsin30−(−mvsin30)=2mv21=mv
Hence the answer is B.mv
Note:
When the object is on the air, the only force acting on the body is the force due to gravitation, which pulls the object back to the surface at the speed of acceleration due to gravity. Note that the range of the projected body is greater than the distance the body will cover, when dropped from the same height.
