Question
Question: A potentiometer wire of length 10 m and resistance \[30\text{ }\Omega\] is connected in series with ...
A potentiometer wire of length 10 m and resistance 30 Ω is connected in series with a battery of emf 2.5 V, internal resistance 5 Ω, and an external resistance R. If the fall of potential along the potentiometer wire is 50μVmm−1, then the value of R is found to be 23n Ω. What is n?
Solution
At first, we have to understand which system is given. Accordingly, write all given information and using standard formulas, calculate the required answer. Potential gradient is the ratio of potential difference and the length of potentiometer wire.
Complete answer:
Let I be the current in the circuit. E be emf, r is internal resistance and Rs is the resistance of wire connected in series with battery.
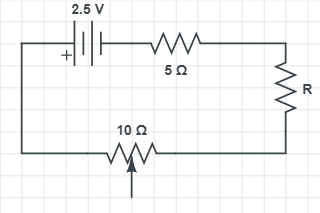
We know that the equation of emf,
E=I(R+Rs+r)
So, we can rearrange it to determine current I as
I=(R+Rs+r)E..........(1)
The potential gradient k of the wire is
k=LIRs......(2)
where L is the length of the potentiometer wire.
Substituting value of I from equation (1) in equation (2) we get,
k=(R+Rs+r)LERs..........(3)
Here it is given that, L=10m, E=2.5V, r=5Ω, Rs=30Ω, k=50μVmm−1, R=23nΩ
Putting all these values in equation (3) we get,
10−350×10−6=(R+30+5)102.5×30
Solving above equation and doing correct calculations we get,
