Question
Question: A potentiometer wire has a resistance per unit length \(0.1\Omega {m^{ - 1}}\). A cell of e.m.f \[1....
A potentiometer wire has a resistance per unit length 0.1Ωm−1. A cell of e.m.f 1.5V balances against 300cm length of the wire. Find the current through potentiometer wire.
Solution
The current is passed through a uniform wire, there is a potential drop across the portion of the wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion.
Formula used:
The current through potentiometer wire I=lrε
Where ε is the emf of the cell, r is the resistance per unit length, l is the balancing length.
Complete step by step answer:
Complete step by step answer:
Given, emf of the cell.
⇒ε=1.5V
Resistance per unit length,
⇒r=0.1Ωm−1
Balancing length,
⇒l=300cm=3m
When the given network or circuit is balanced then there is no current through the galvanometer.
Which implies, the potential difference across the initial length of the wire to the point where it shows balancing length is equal to emf of the secondary cell that is 1.5V
Potential difference across AC = (current through potentiometer wire) × (resistance of the potentiometer wire of length AC).
Therefore, r is the resistance per unit length of the wire and I is the current passing through wire, then
Ilr=ε
I=lrε
⇒3×0.11.5
∴5A
Thus, the current through potentiometer wire is 5A.
Additional information:
The potentiometer consists of a wooden board on which many numbers of uniform wires are stretched parallel to each other. The wire is made of manganin or nichrome. The end terminals of the wires are provided with a connecting screw. A meter scale is fixed on the wooden board parallel to wires. A jockey or sliding contact is provided with the arrangement. The jockey has a pointer which can slide over the meter scale. In Figures A and C are the ends of the wire.
if a wire of uniform area of cross-section is carrying a steady current then fall of potential across any portion of the wire is directly proportional to the length of that portion. ε=ϕl
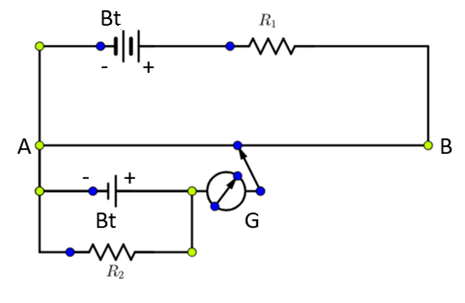
In the diagram Bt- batteries, R1R2- Resistances, G- galvanometer.
Note:
The potentiometer is basically measuring the potential difference between the two points but on this basis, it can be used to make several other measurements.
The main advantage of this potentiometer is that it can measure potential differences without drawing a current.
