Question
Question: A point source of light is placed at 2f from a converging lens of focal length f. A flat mirror is p...
A point source of light is placed at 2f from a converging lens of focal length f. A flat mirror is placed on the other side of the lens at a distance d such that the rays reflected from the mirror are parallel after passing through the lens again. If f=30 cm, then d is equal to
A. 15 cm
B. 30cm
C. 45 cm
D. 75 cm
Solution
Hint:
Knowledge of which kind of image is formed, when the object is placed at different distances with respect to the lens and mirror is also necessary.
Step by step solution:
Let’s make the ray diagram of the question first.
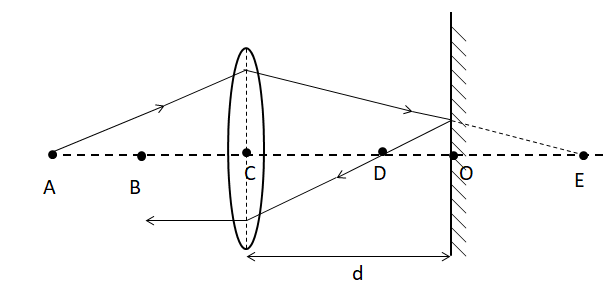
The object is placed at A. The point C denotes the center of the convex lens. Point B is at a distance of focal length f with respect to the lens. Point D denotes a point of intersection with the horizontal when the ray is reflected back. Point E refers to the point where a virtual image is created.
Therefore we know that distanceAC=2f, BC=f.
Now, let’s consider the mirror wasn’t there. Then, since the object is at 2f with respect to the center of the lens, an image of the same dimension is formed on the other side of the lens.
Therefore, since E is the original point where the ray would have reached without the mirror, hence, distanceCE=2f.
Now considering the mirror and the reflected ray, the reflection happens such that the ray upon interacting with the lens becomes a parallel ray. For this to occur, the ray must have passed through the point which is at f distance from the lens.
Therefore, distanceCD=f.
Using the values of CE and CD, we can get the value ofDE=CECD.ThereforeDE=2f−f,that is, distanceDE=f.
Since a plane reflecting mirror is used, the ray reflecting and the imaginary being transmitted would be travelling the same amount of distance when it hits the horizon. That is, OD = OE.
Using this condition and the above value ofDE=f,$$$$OD+OE=f,which isOD=2f.
The distance required to find out is the distance isCD+OD=f+2f=23f.
Given, that f=30cm. Therefored=23×30=45cm.
Note:
The question is about converging or convex lens, it shouldn’t be misinterpreted as diverging or convex lens.
Making the correct ray diagram using the information given is important.
