Question
Question: A plot given shows P – T curves (where P is the pressure and T is the temperature) for two solvents ...
A plot given shows P – T curves (where P is the pressure and T is the temperature) for two solvents X and Y, and isomolar solutions of NaCl in these solvents. NaCl completely dissociates in both the solvents. In addition to an equal number of moles of non-volatile solute S in equal amount (in Kg) of these solvents, the elevation of the boiling point of solvent X is three times that of solvent. Solute S is known to undergo dimerization in these solvents. If the degree of dimerization is 0.7 in solvent Y, the degree of dimerization in solvent X is:
Solution
The elevation in the boiling point is equal to the product of ionization of solute, molality, and molal elevation constant. The formula is ΔTb=i x m x Kb. The value of i can be calculated by the reaction 2(S)→S2.
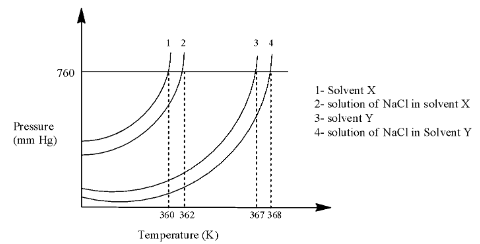
Complete answer: In the graph, there are four lines in which the first 2 lines are used for solvent X and the last two lines are used for solvent Y.
Line 2 is at 362 K and line 1 is at 360 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
ΔTb(X)=362−360=2
Line 4 is at 368 K and line 3 is at 367 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
ΔTb(Y)=368−367=1
According to the formula, we can write for X and Y as:
ΔTb(X)=i x mNaCl x Kb(X)
ΔTb(Y)=i x mNaCl x Kb(Y)
When we divide the above equations, we get:
Kb(Y)Kb(X)=2
Since the dimerization takes place, we can write the equation as:
2(S)→S2
After the equilibrium is attained, the concentration of S will be 1−α and the value of S2 will be 2α
So, the value of i, will be:
i=(1−2α)
Now, putting these values in the elevation in boiling point equation, we get:
ΔTb(X)=(1−2α1) x mNaCl x Kb(X)
ΔTb(Y)=(1−2α2) x mNaCl x Kb(Y)
In the question, it is given that:
ΔTb(X)=3 x ΔTb(Y)
Combining, all these we can write:
(1−2α1) x Kb(X)=3 x (1−2α2) x Kb(X)
2 x (1−2α1)=3 x (1−2α2)
a2 = 0.7 and a1 = 0.05.
The degree of dimerization of solvent X is 0.05.
Note: Don’t get confused between the formulas ΔTb=i x m x Kb and ΔTb= m x Kb, the former is used when there is any electrolyte or ionic compound is present in the solution and the latter is used when covalent compound is present.
