Question
Question: A Pitot tube (shown in the figure )is mounted along the axis of a gas pipeline whose cross-sectional...
A Pitot tube (shown in the figure )is mounted along the axis of a gas pipeline whose cross-sectional area is equal to S. Assume the viscosity to be negligible, the volume of gas flowing across the section of the pipe per unit time, if the difference in the liquid columns is equal to Δh and the densities of the liquid and gas are ρo and ρ respectively is Q=SρxΔgρog find the value of x.
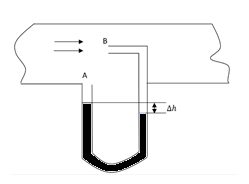
Solution
Apply the Bernoulli principle at the two cross-sections A and B and take the difference of the pressures at A and B equal to ρogΔh get the value of the volume of gas flowing per unit time into the section B and thus the value of the x required.
Complete step by step solution:
We have two cross-sections A and B and the gas flows through the cross-section B.
Now the Bernoulli principle can be stated as:
At any cross section the P+21ρv2 = constant.
Now let us consider the volume of gas flowing across section B per unit time as VB
And the value of the velocity of the gas flowing through section A is zero.
Let the pressure at section A be PA and the pressure at section B is PB
The density of the gas is ρ
Applying the Bernoulli principle in section A we get :
PA+21ρVA2 = constant
Similarly applying Bernoulli principle at section B we get:
PB+21ρVB2 = constant
Taking VB = V and VA = 0 we get from the about two equations we can get the difference in pressures as
PA−PB=21ρv2
Now we know the difference in pressure at A and B should be equal to
we get PA−PB=21ρv2=ρogΔh
v=ρ2Δhρog
The volume of the per unit time given area of the cross-section is: Q=S×v
So we get
Q=Sρ2Δhρog
Thus we got the value of using the Bernoulli principle as 2 .
Note: Here we neglected the height difference between the section a and b. The possible mistakes that we can make in this kind of problem are that we may consider the height difference between sections A and B which will lead to mistakes and time-consuming.
