Question
Question: A pitot tube is inserted in an air flow (at STP) to measure the flow speed. The tube is inserted so ...
A pitot tube is inserted in an air flow (at STP) to measure the flow speed. The tube is inserted so that it points upstream into the flow and the pressure sensed by the tube is stagnation pressure The static pressure is measured at the same location in the flow using a wall pressure tap if the pressure difference is 30mm of mercury, determining the flow speed.
A) 80.8m/s
B) 40m/s
C) 10.23m/s
D) None of these
Solution
A pitot tube works on principle of bernoulli's theorem basically we convert kinetic energy of flowing fluid into the pressure energy inside the pitot tube.
Bernoulli's equation is P+21ρv2+ρgh= constant
Step by step solution:
Pitot tube is an L shaped tube by which we can find the velocity of flowing fluid as shown in figure
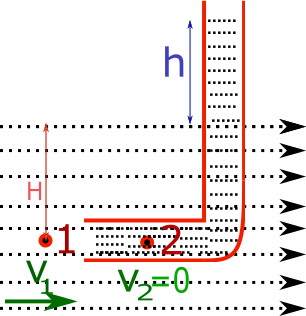
We take 2 point at the same horizontal level point 1 and point 2
Pressure at point 1 is P1 and velocity is v1 and at point 2 inside the Pitot tube has pressure P2 and velocity of fluid v2=0 inside the tube this condition is called stagnation point.
So we apply Bernoulli’s theorem for point 1 and point 2
Energy at point 1= energy at point 2
⇒P1+21ρv12+ρgh=P2+21ρv22+ρgh
As we know point 1 and point 2 is at same horizontal level so ρgh term will vanish
⇒P1+21ρv12=P2+21ρv22
At stagnation point v2=0
⇒P1+21ρv12=P2
⇒21ρv12=P2−P1 .......... (1)
In our question P2−P1 is given 30 mm of Hg
Calculate pressure due to 30 mm column of Hg
⇒P2−P1=ρHggh
⇒P2−P1=30×10−3×13600×10
Solving this
P2−P1=3999.67N/m2
Put this in equation (1)
⇒21ρv12=3999.67
⇒v12=ρ2×3999.67
Density of air at STP is ρ=1.225kg/m3
⇒v12=1.2252×3999.67
Solving this
⇒v12=6530.07
⇒v1=6530.07
∴v1=80.80m/sec
Hence option A is correct
Note: The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the fluid flow as this tube contains fluid; a pressure can be measured; the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue; this pressure is the stagnation pressure . This comes due to loss in kinetic energy or dynamic pressure.
