Question
Question: A piece of wood is taken deep inside a long column of water and released. It will move up: A. W...
A piece of wood is taken deep inside a long column of water and released. It will move up:
A. With a constant upward acceleration
B. With a decreasing upward acceleration
C. With a deceleration
D. With a uniform velocity
Solution
Buoyancy is the effect of a fluid due to which a force acts on the object. This effect acts opposite to the motion of the object. It varies according to the position and weight of the object.
Here, in this question, we need to determine the nature of the motion of the object in which the object is already submerged deep-inside the water and is being released from there. For this, we need to use the properties of the buoyancy, as discussed.
Complete step by step answer:
Mathematically, the Buoyant force is given as W=ρgV where, ρ is the density of the water in which the object is placed, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and V is the volume of the water displaced due to the insertion of the object.
So, here in this case, when the piece of wood is released, then two forces act on it; the first one is the Gravitation Force (acting downwards), and the second is Buoyancy Force (acting upwards). The net force here is acting upwards as the density of the wooden piece is less than that of water, which is given as FN=Fb−Fg. So, the velocity of the wooden piece is also upwards.
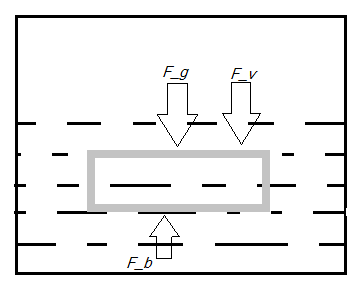
Now, as the wooden piece rising upwards in the water, the viscous force acting on it (towards downwards) also increases and hence, the total force on the wooden block will be now reduced to FN=(Fb−Fg)−Fv which shows that that the velocity is decreasing as the wooden piece is coming towards the surface of the water.
Hence, we can say that the wooden piece will have a decreasing upward acceleration when released for the full-submerged liquid.
Option B is correct.
Additional Information: Viscosity is the measure of the extent to which fluid flow is redistricted, and its unit is newton-second per square meter, which is usually expressed as Pascal-second. The viscosity of liquids decreases rapidly with an increase in temperature. Viscous force is the force acting between the layers of flowing fluid. It is the rate at which the fluid velocity changes its space.
Note: Students should be aware of the buoyant force and the viscous force. Moreover, students should be aware while applying the directions to the force. It is worth noting down here that the deceleration is the negative acceleration and not the decreasing acceleration.
