Question
Question: A piece of liver tissue is homogenized in a laboratory and the homogenate is subjected to sequential...
A piece of liver tissue is homogenized in a laboratory and the homogenate is subjected to sequential centrifugation at increasing speeds ( expressed in xg ). Centrifugation is used to separate subcellular components based on size and density. The steps carried out in the experiment are shown. Sediments 1, 2 and 3 would most likely contain.
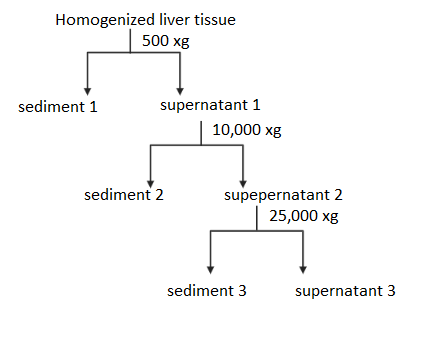
A) 1: Nuclei, 2: Ribosomes, 3: Mitochondria
B) 1: Nuclei, 2: Mitochondria, 3: Lysosomes
C) 1: Lysosomes, 2: Mitochondria, 3: Nuclei
D) 1: Ribosomes, 2: Nuclei, 3: Mitochondria
Solution
Centrifugation is a mechanical method involving the use of centrifugal force according to its scale, shape, density, medium viscosity and rotor speed to remove particles from a solution. The liver homogenate is a tissue of the liver in which its cells, releasing organelles and cytoplasm, have been mechanically disrupted. Each cell is composed of cell organelles such as nuclei, mitochondria, ER, lysosomes and many more.
Complete answer:
A centrifuge operates by using the sedimentation principle; substances separate according to their density under the influence of gravitational force (g-force). Various forms of separation, including isopycnic, ultrafiltration, the gradient of density, phase separation and pelleting, are known. Based on size and density, centrifugation is used to isolate subcellular components. The larger the density, the more quickly it moves. In order to separate various subcellular components from the homogenate, differential centrifugation uses different velocities. The heaviest subcellular elements, i.e. nuclei, would settle first when homogenized liver tissue is centrifuged at 500 xg. The second heavier sub-cellular component, which is mitochondria, will settle when the supernatant is again centrifuged at 10000 xg. The lightest sub-cellular part, that is, lysosomes, will settle when the supernatant is centrifuged at a very high speed of 25000 xg. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
So, option B is the correct answer.
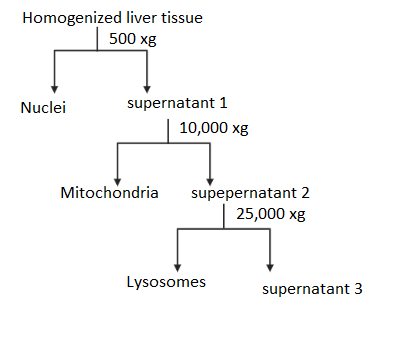
Note: The order of sedimentation is usually (from most to least dense) with regard to the major components found in cells: nuclei, mitochondria, lysosomes, plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum and contractile vacuoles. Animal tissue is homogenized more readily than plant tissue since there are no cell walls, and soft and reasonably homogeneous tissue is the liver in particular.
