Question
Question: A perfect diode is connected to an a.c. Determine the limits within which the voltage between the an...
A perfect diode is connected to an a.c. Determine the limits within which the voltage between the anode and the cathode varies.
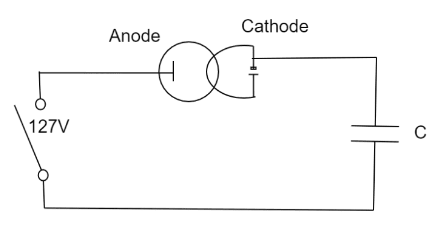
Solution
Plot the time dependences of the external voltage Uex (t), the current in the circuit Ic (t), the voltage across the capacitor Uc (t), and the voltage across the diode Ua (t). by this we will get the value of the required voltage.
Complete answer:
A diode is a nonlinear, unidirectional device. When you connect it to an AC supply, you're putting both positive and negative potential to it. However, after forward break over voltage, the diode only conducts in forward mode, that is, from anode to cathode (when positive). As a result, it will only supply output for the positive half of the cycle and none for the negative half. If the diode is linked in the opposite direction, the result is the opposite. Half wave rectification is the name given to this phenomena, and the device's name is changed to half wave rectifier.
Plotting the time dependences of the external voltage Uex (t) , Ic (t) is the current in the circuit (which only flows in one direction while the diode is open), the voltage across the capacitor, Uc (t), and the voltage across the diode, Ua (t).
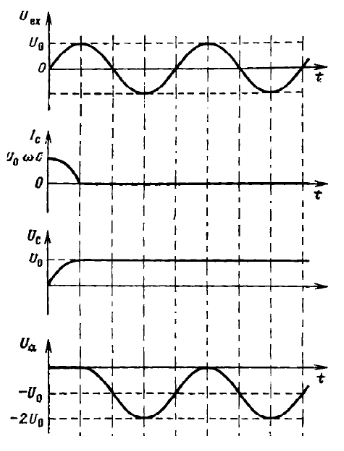
As a result, the voltage between the anode and the cathode can range from 0 to −2U0 .
Note:
When a diode is forward biased and behaves as a perfect conductor with zero voltage across it, it is called an Ideal Diode. When the diode is reversed biased, it works as a perfect insulator, allowing no current to pass through.
