Question
Question: A meter-bridge is based on the principle of A. Wheatstone bridge B. Variation of resistance with...
A meter-bridge is based on the principle of
A. Wheatstone bridge
B. Variation of resistance with temperature
C. Galvanometer
D. None of these
Solution
Meter bridge consists of 4 resistance in bridge form in which the ratio of two resistance in one half of the bridge is equal to the ratio of the other two resistance, then there will be no flow of current between those edges containing the resistors.
Formula used:
Balanced condition for a meter bridgeQP=SR
Where P,Q, R, S are the 4 resistors of the bridge
Resistance per unit length,σ=LengthResistance
Complete step by step answer:
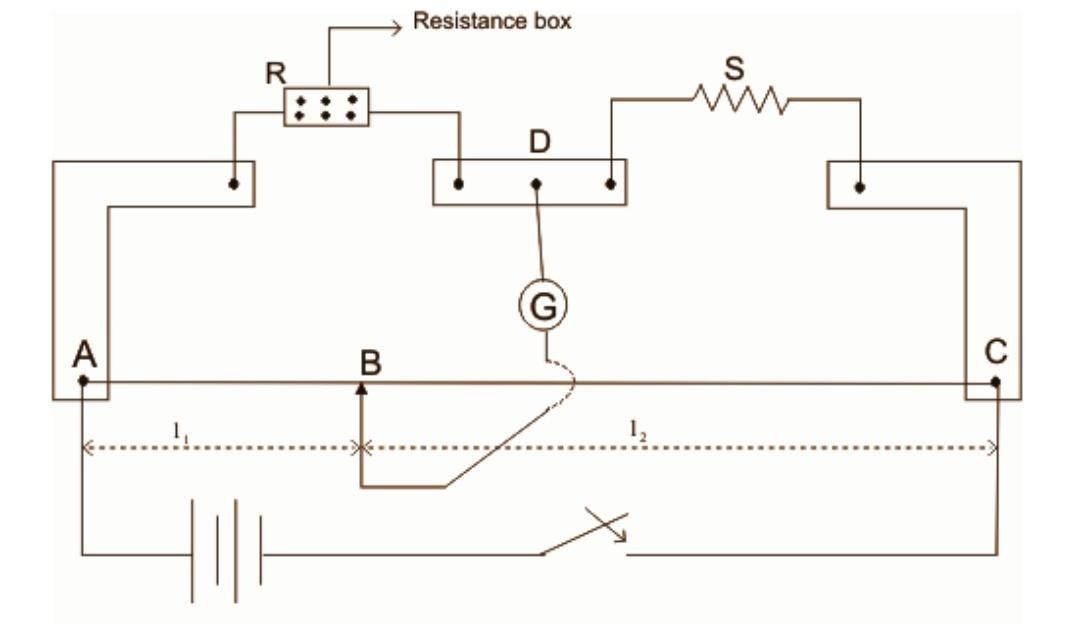
Meter bridge is used to measure the value of unknown resistance, It is based on the principle of Wheatstone bridge i.e. when the bridge is balanced then
QP=SR.
Where P= resistance of wire AB, Q= resistance of wire BC.
So correct option is A.Wheatstone Bridge
Additional Information:
Meter bridge consists of one-meter long manganin wire having uniform cross-section, which is stretched along a meter scale fixed over a wooden board and with its two ends connected to two L-shaped copped strips at A and C. Another copper strip is fixed in between these two strips to provide the gap for connection of resistance box R and resistance S. An emf source is connected across AC. A movable jockey in series with a galvanometer is connected across points B and D.
For a suitable resistance, the jockey is moved along the wire AC, until there is no deflection in the galvanometer. This is the balanced condition and point B is called the null point.
For balanced condition QP=SR
Total length of wire AC=100cm,let AB=lcm,then BC=(100−l)cm.As the wire has uniform cross section so
Resistance of wire α length of wire
So, QP=Resistance of wire BCResistance of wire AB
If σ=resistance per unit length,then resistance of AB is σland resistance of BC is σ(100−l)
So above equation becomes
QP=σ(100−l)σl=100−ll
As QP=SR, so
SR=100−ll
Or , S=100−llR
Knowing the value of l and R unknown resistance S can be measured.
Note:
Meter bridge works on the balanced condition of the Wheatstone bridge. During a lab experiment of a meter, the bridge adjusts the value of the resistance box and moves the jockey to get a null deflection. Then calculate the value of L1 and L2. After substituting these values in the Meter Bridge equation above you can calculate the value of unknown resistance S.
