Question
Question: (a) Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Write...
(a) Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of polymerase chain
reaction (PCR). Write the role of primers and DNA polymerase in PCR.,
(b) Give the characteristic feature and source organism of the DNA polymerase in PCR.
Solution
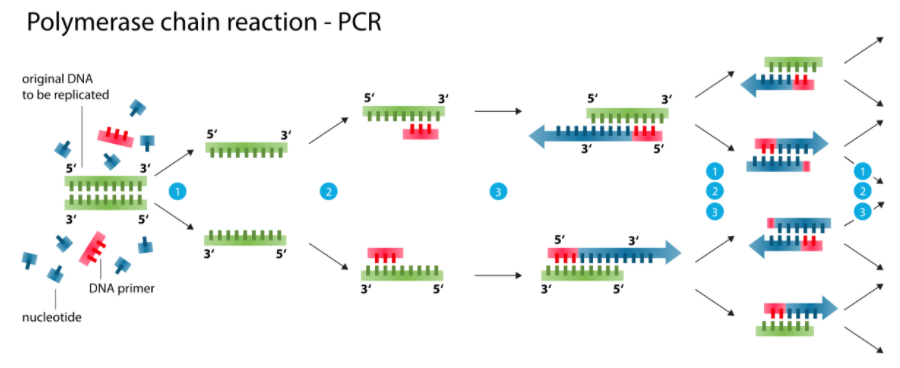
Hint:- PCR is based on the use of DNA polymerase's ability to synthesise new DNA strands complementary to the template strand provided. Since a nucleotide can only be added to a preexisting 3'-OH group by DNA polymerase, it requires a primer to which the first nucleotide can be added.
Complete step-by-step solution:-
In any cycle of polymerase chain reaction , two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase are needed.
Role of primers and DNA polymerase: To begin the functioning of DNA polymerase, primers are needed. Using the nucleotides given in the reaction and the genomic DNA as the template, DNA polymerase extends the primers. The DNA section can be amplified up to around a billion times. The use of a thermostable DNA polymerase, which remains active during high-temperature induced denaturation of double-stranded DNA, achieves such repeated amplification through the use of a thermostable.
Taq polymerase, which is derived from a bacterium called Thermus aquaticus, is the DNA polymerase used in the PCR reaction. During the high-temperature induced denaturation of double-stranded DNA, it stays active.
Additional Information:
The PCR reaction begins exponentially to produce copies of the target sequence. Extrapolation back to determine the starting quantity of the target sequence present in the sample is only feasible during the exponential step of the PCR reaction. The PCR reaction gradually ceases to amplify the target sequence at an exponential rate because of polymerase reaction inhibitors contained in the sample, reagent restriction, accumulation of pyrophosphate molecules, and self-annealing of the accumulating substance, and a "plateau effect" occurs, rendering the end point quantification of PCR products unreliable.
Note:-
In medical and biological research laboratories, PCR is a popular method. It is used for sequencing, for detecting the presence or absence of a gene to help identify pathogens during infection, and when producing forensic DNA profiles from small samples of DNA in the early stages of processing DNA.
