Question
Question: A mass m moves with a velocity v and collides inelastically with another identical mass. After the c...
A mass m moves with a velocity v and collides inelastically with another identical mass. After the collision, the first mass moves with velocity 3v in a direction perpendicular to the initial direction of motion. Find the speed of the second mass after the collision
A. 32v
B. 3v
C. v32
D. The situation of the problem is not possible without external impulse
Solution
In extreme cases of inelastic collision, the masses stick together. In an inelastic collision, the kinetic energy is not conserved; only the total energy is conserved. Almost all macroscopic collisions are inelastic. Remember that after sticking together, the composite body moves with one velocity v1, and the mass will be the sum of both m1+m2.
Complete step by step answer:
Refer to the below figure for a proper explanation. The velocities are shown before and after the collision. The upward Y direction's velocity is taken as positive and the velocities in the downward Y direction are taken as negative.
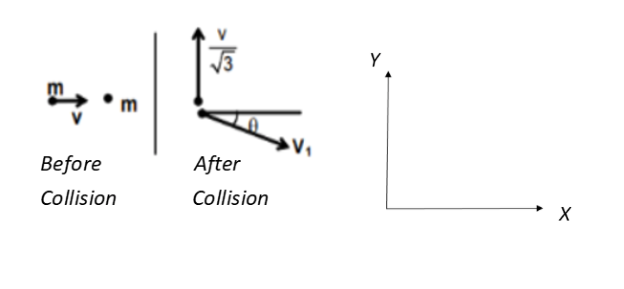
We know that the momentum is conserved to apply the conservation of momentum in the X-direction.
mv=mv1cosθ v=v1cosθ......(1)
We will now apply the conservation of momentum in the Y direction.
0=3mv−mv1sinθ 3v=v1sinθ......(2)
Now squaring and adding equation (1) and (2), we get,
