Question
Question: A long metallic bar is carrying heat from one of its ends to the other and under a steady state. The...
A long metallic bar is carrying heat from one of its ends to the other and under a steady state. The variation of temperature q along the length x of the bar from its hot end is best described by which of the following figures?
A.
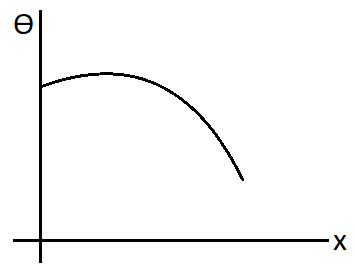
B.
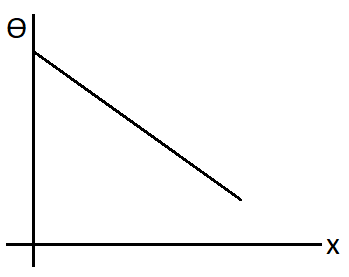
C.
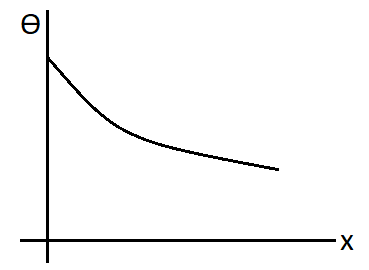
D.
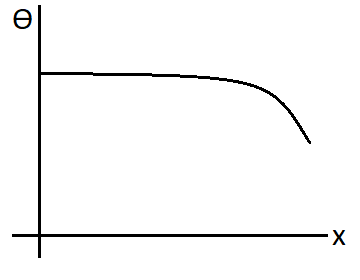
Solution
From the formula for the rate of the heat flow, we can find the formula in the terms of the temperature gradient at the hot end and the length of the rod. From that relation we can see how the temperature depends on the length. We can find our graph from there.
Formula used:
In this solution we will be using the following formula,
⇒dtdQ=−KAdxdθ
where dtdQ is the rate of heat flow,
K is the thermal conductivity,
A is the area of cross section
and −dxdθ is the thermal gradient.
Complete step by step solution:
In the question we are given that a metallic bar is carrying heat from one of its ends to the other. So we can write the rate of flow of heat by the formula,
⇒dtdQ=−KAdxdθ
Here the −dxdθ is the thermal gradient.
The negative sign is present because, as the distance from the hot end increases the temperature of the rod decreases.
Now in the question we are told that the metallic bar carrying the heat is under a steady state. So the thermal gradient of the rod will be constant. Let us name this constant as C.
Therefore, we can write,
⇒−dxdθ=C
Now we can take the denominator of the LHS to the RHS and get,
⇒dθ=−Cdx
Now we can integrate on both the sides. So we have,
⇒∫dθ=−∫Cdx
The constant C will come out of the integration,
∫dθ=−C∫dx
On integrating we get,
⇒θ=−Cx+D
Here we can see the dependence of the temperature θ on the distance. This equation can be compared to the equation of straight line given by
⇒y=mx+C
So we can see that the slope will be negative for this plot. Hence the correct plot will be
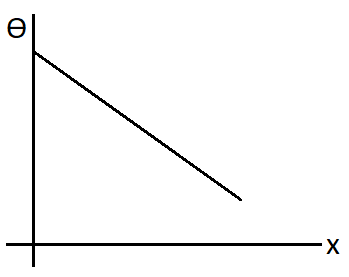
Therefore, option (B) is correct.
Note:
The process by which the rod gets heated up is called conduction. When one end of the rod is heated, the molecules at that end acquire energy from the heat and start moving faster. These fast moving molecules collide with the adjacent molecules and transfer some part of their energy. Through his process, the heat gets transferred.
