Question
Question: A lone pair of electrons in an atom implies: A. A pair of valence electrons B. A pair of electro...
A lone pair of electrons in an atom implies:
A. A pair of valence electrons
B. A pair of electrons
C. A pair of electrons involved in bonding
D. A pair of electrons not involved in bonding
Solution
The lone pair of electrons in the atom is the valence set of electron pairs settled above the central atom after the sharing of valence electrons by the atom with their neighboring atoms to form a chemical bond takes place. This results in the formation of covalent bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
The molecule is formed by the atoms by sharing electrons. Each atom shares electrons to form a chemical bond.
The chemical bond formed between the atoms is called a covalent bond.
When one electron is shared by each atom then a single bond is formed. Example: methane CH4.
When two electrons are shared by each atom then a double bond is formed. Example: ethene C2H4.
When three electrons are shared by each atom then a triple bond is formed. Example: ethyne C2H2.
In some molecules, all the electrons do not take part in the bonding process.
For example Ammonia, chemical formula NH3.
Ammonia is formed of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms.
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7.
The electronic configuration of nitrogen is [He]2s22p3.
Nitrogen has a total of five electrons in the outermost orbitals out of which three unpaired electrons in p-orbital, so it can share its three electrons to form bonds with neighboring atoms.
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1.
The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s1.
As three hydrogen atoms are present. It can share its three electrons with the neighboring atom to form a chemical bond.
Two electrons of nitrogen do not take part in bond formation.
Lewis dot structure of ammonia is shown below.
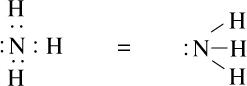
The electrons which are shared by the atoms to form the chemical bond are called a bonding pair of electrons and the electron which does not involve bond formation are called lone pairs of electrons.
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note:
The lone pair of electrons localized at the central atom forms a bond angle that has a different bond angle than the tetrahedral 109.5∘because the bonding electron pair utilizes less space than the nonbonding electron pair. Thus, the bond angle in ammonia is 107∘.
