Question
Question: A line segment has endpoints at \[\left( {1,2} \right)\] and \[\left( {3,1} \right)\] . The line seg...
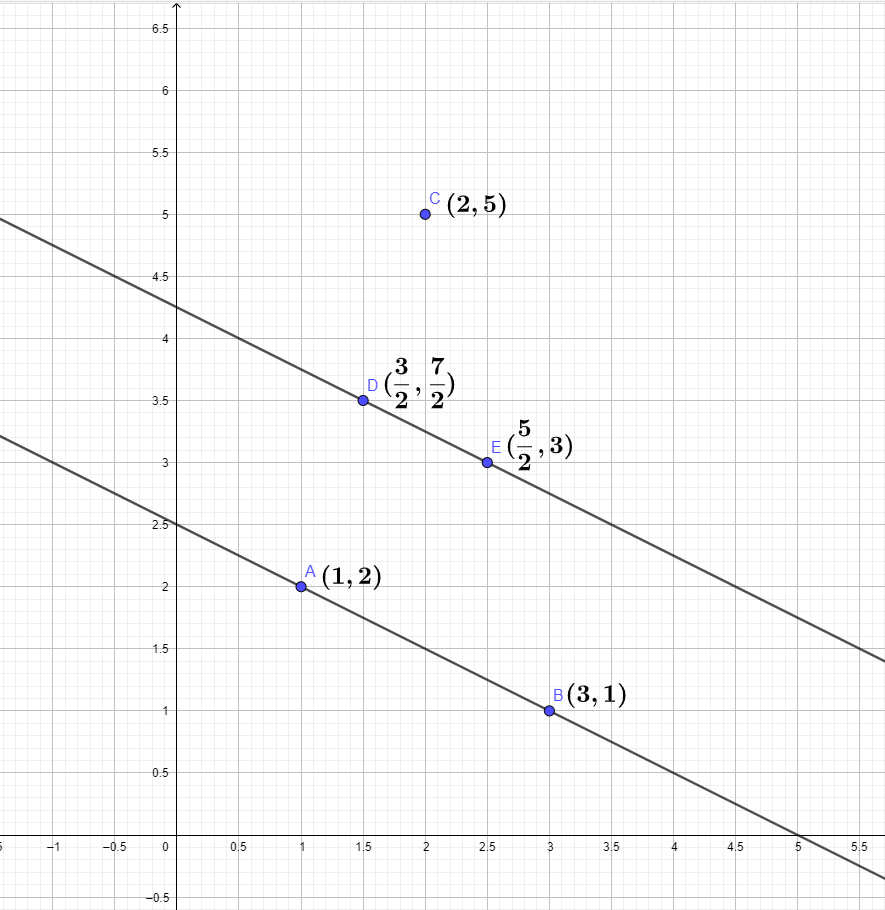
A line segment has endpoints at (1,2) and (3,1) . The line segment is dilated by a factor of 21 around (2,5) .What are the new endpoints and length of the line segment?
Solution
In order to solve this question, we will use the concept that if a point X of coordinate (a,b) is dilated by a factor n around the point of coordinate (h,k) , then after dilation the new position of point will be X′=(n(a−h)+h, n(b−k)+k) .Firstly we will let A and B be the two endpoints of the line segment. After that we will let A′ and B′ be the new endpoints of the line segment after dilation and find them by substituting the values in the above formula. And finally, we will find the length of the dilated line segment using distance formula i.e., d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2 .And hence we will get the required result.
Complete answer: :
Let A and B be the two endpoints of the line segment.
which means A(1,2) and B(3,1) be the two endpoints of the line segment.
And let A′ and B′ be the two new endpoints of the line segment.
Now we know that
If a point X of coordinate (a,b) is dilated by a factor n around the point of coordinate, (h,k) then after dilation the new position of point will be
X′=(n(a−h)+h, n(b−k)+k)
This means
X(a,b)=dilated nX around (h,k)X′(n(a−h)+h,n(b−k)+k)
Now it is given that
line segment is dilated by a factor of 21 around (2,5)
which means n=21 and (h,k)=(2,5)
Using the formula, we get
A(1,2)=dilated 21X around (2,5)A′(21(1−2)+2, 21(2−5)+5)
⇒A(1,2)=dilated 21X around (2,5)A′(2−1+2, 2−3+5)
On simplification, we get
A(1,2)=dilated 21X around (2,5)A′(23,27)
which means the first new endpoint is A′(23,27)
Similarly,
B(3,1)=dilated 21X around (2,5)B′(21(3−2)+2, 21(1−5)+5)
⇒B(3,1)=dilated 21X around (2,5)B′(21+2, 2−4+5)
On simplification, we get
B(3,1)=dilated 21X around (2,5)B′(25,3)
which means the second new endpoint is B′(25,3)
Therefore, the new endpoints are A′(23,27) and B′(25,3)
Now we know that
Distance formula, d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2
Therefore, the length of the dilated line segment will be
A′B′=(25−23)2+(3−27)2
⇒A′B′=(1)2+(2−1)2
⇒A′B′=45
We know that ba=ba
Therefore, we have
⇒A′B′=45=25
We know that 5=2.236
⇒A′B′=22.236=1.118
Hence, the new endpoints are A′(23,27) and B′(25,3)
and the length of line segment A′B′=1.118
Note:
Alternative way to solve this problem is:
If x0 is the dilation centre, x1 and x2 are the coordinates of the endpoints of the line segment and λ is the factor of dilation, then the position of new endpoints will be given by:
x1′=x0+λ(x1−x0) and x2′=x0+λ(x2−x0)
So, here x0=(2,5), x1=(1,2), x2=(3,1), λ=21
Therefore, we get
x1′=(2,5)+21((1,2)−(2,5))
⇒x1′=(2,5)+21(1−2,2−5)
⇒x1′=(2,5)+(2−1,2−3)
⇒x1′=(23,27)
And
x2′=(2,5)+21((3,1)−(2,5))
⇒x2′=(2,5)+21(3−2, 1−5)
⇒x2′=(2,5)+(21,−2)=(25, 3)
Hence, the new endpoints are x1′=(23,27) and x2′=(25,3)
Now, the length of the dilated line segment will be
x1′x2′=(25−23)2+(3−27)2
⇒x1′x2′=25=22.236
⇒x1′x2′=1.118
Hence, the length of the line segment x1′x2′=1.118
Hence, we get the required results.
