Question
Question: A light and inextensible string of length \(L = 20 m\) tired between two nails, supports a frictionl...
A light and inextensible string of length L=20m tired between two nails, supports a frictionless pulley of weight Wp=102N from which a block of weight Wb=102N is also suspended as shown in the figure. The nails are fixed in a level a distance x=102m apart. Radius of the pulley is r=10cm. How much normal reaction per unit of its length does the string apply on the pulley.
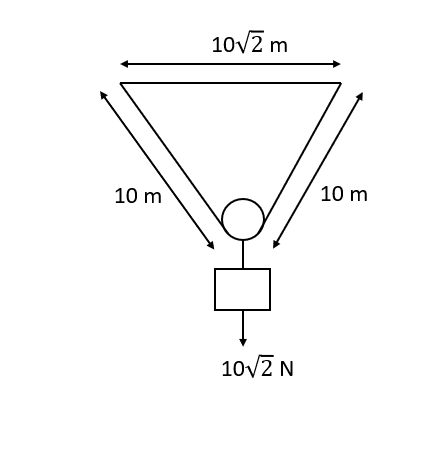
Solution
A force is acting normally on two surfaces in touch with each other. It is an estimation of the force keeping the two surfaces together. The higher the normal reaction force, the higher the value of limiting resistance. If weight is the only upward force acting on an object moving on a uniform surface, the normal reaction force is equivalent in magnitude but opposite in direction to the weight. Friction, therefore, is enhanced by increasing the weight.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: Radius of pulley =10cm=0.1m
dl: length of arc
dθ=rdl
dl=0.1dθ
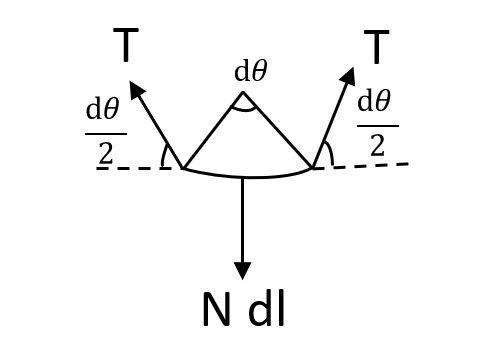
Now, we will balance the forces vertically.
2Tsin2dθ=Ndl
For small angle, it will become,
2T2dθ=Ndl
Tdθ=Ndl
It will give,
N=10T ……(1)
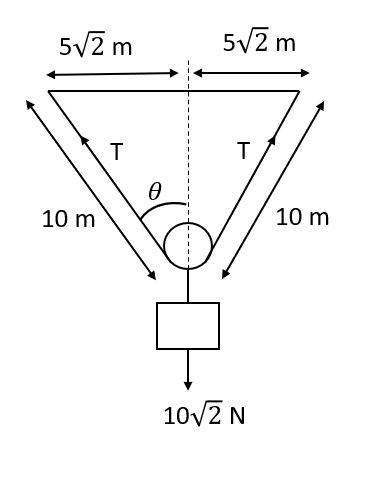
Now we will find sine of angle in the above,
sinθ=1052
⟹sinθ=21
It will give,
θ=45∘
Now, we will find the value of T:
2Tcos45∘=Wp+Wb
⟹2T×21=202
⟹T=20N
Now we have to find the normal reaction by equation (1).
N=10×20=200N
Thus, the normal reaction per unit of its length on the pulley is 200N.
Note: The force holding a load is upright to the surface of touch between the load and its provider, and this force is termed a normal force, often shown with the symbol N. The word normal indicates normal to a surface. The normal force is not forever equal to the object's weight if other forces act on the object or if the object is quickening so that the whole force is not zero.
