Question
Question: (a) Identify the figure. (b) Name the initial cell from which this structure has developed (c) D...
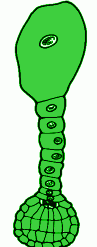
(a) Identify the figure.
(b) Name the initial cell from which this structure has developed
(c) Draw the next mature stage and label the parts.
Solution
Double fertilization is a complex fertilization mechanism in flowering plants that involves the joining of female gametophyte with two male gametes resulting in triple fusion to produce endosperm and embryo.
Complete answer: Double fertilization begins when a pollen grain sticks to the stigma of the pistil and germinates due to the moisture present on the stigma. Pollen grain forms a pollen tube then extends to the ovary and penetrates through the micropyle opening in the ovule. This pollen then releases two sperm cells in the megagametophyte. The cells in the unfertilized ovule are present as 3 antipodal cells, 2 polar central cells, 2 synergids, and 1 egg cell. One sperm fertilizes with the egg cell to produce a zygote and the other sperm cell fuses with polar central cells to produce a triploid primary endosperm nucleus. After double fertilization endosperm and embryo thus formed matures into seeds and fruit. The embryo develops at the micropylar end of the embryo sac where the zygote is present. Most of the zygote differentiates after a certain growth of endosperm. The zygote gives rise to proembryo and further globular, heart-shaped, and mature embryos.
An embryo consists of an embryonal axis and two cotyledons. Epicotyl is the above region of the embryonal axis that terminates at the plumule. Hypocotyl is the cylindrical portion present below the cotyledons that ends at the radicle. The radicle is covered with a root cap.
a. The figure thus given above is of a globular embryo.
b. The initial cell from which the proembryo is developed is the zygote.
c. The next stage is the mature embryo.
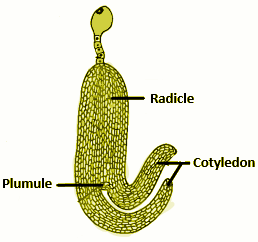
Note: Embryos made of one cotyledon are known as monocotyledonous. The cotyledon in the grass family is known as the scutellum and is situated towards one side of the embryonal axis. At its lower end, the embryonal axis has a radicle and root cap in an undifferentiated sheath called coleorhiza.
