Question
Question: A hydrogen balloon is flying eastward with speed \(12\,m{s^{ - 1}}\).when wind starts blowing from n...
A hydrogen balloon is flying eastward with speed 12ms−1.when wind starts blowing from north to south with the speed 5ms−1,what is the resultant velocity of balloon ?
Solution
To answer this question, we first need to understand what is resultant velocity. The sum of an object's individual vector velocities is its resultant velocity. The scalar product of an object's mass and its acceleration vector equals the sum of the vector forces acting on it.
Complete step by step answer:
As given in this question the speed of the hydrogen balloon and the wind are perpendicular to each other. So, this forms a right-angled triangle with a base of 12ms−1 and a height of 5ms−1. Whereas the resultant velocity is the hypotenuse. So, in order to find out this resultant velocity we have to apply the Pythagoras theorem to get the solution.
According to Pythagoras theorem
H=h2+b2
Here H is the hypotenuse whereas b is the base and h are the height.
So, substituting the values of h and b.
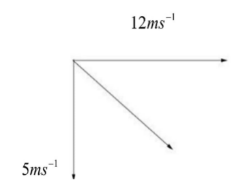
H=52+122
⇒H=25+144
⇒H=169
∴H=13ms−1.
So, the final answer is that the resultant velocity is 13ms−1.
Note: The velocity's sign is determined by the coordinate system used to define the spot. A positive velocity indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction as defined by the coordinate system, while a negative velocity indicates that the object is moving in the opposite direction.
