Question
Question: A hydrocarbon of molecular formula \({{\rm{C}}_{\rm{5}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{10}}}}\) could be a: This ...
A hydrocarbon of molecular formula C5H10 could be a:
This question has multiple correct options
A. Monosubstituted alkene
B. Disubstituted alkene
C. Trisubstituted alkene
D. Tetrasubstituted alkene
Solution
We know that a hydrocarbon is an organic compound in which carbon and hydrogen atoms present. Some examples of hydrocarbon are methane, ethane etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The molecular formula of the compound is C5H10. We have the identify the of substitution possible in C5H10. A monosubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms bonded to only one carbon atom.
Now we draw the monosubstituted alkene of C5H10.
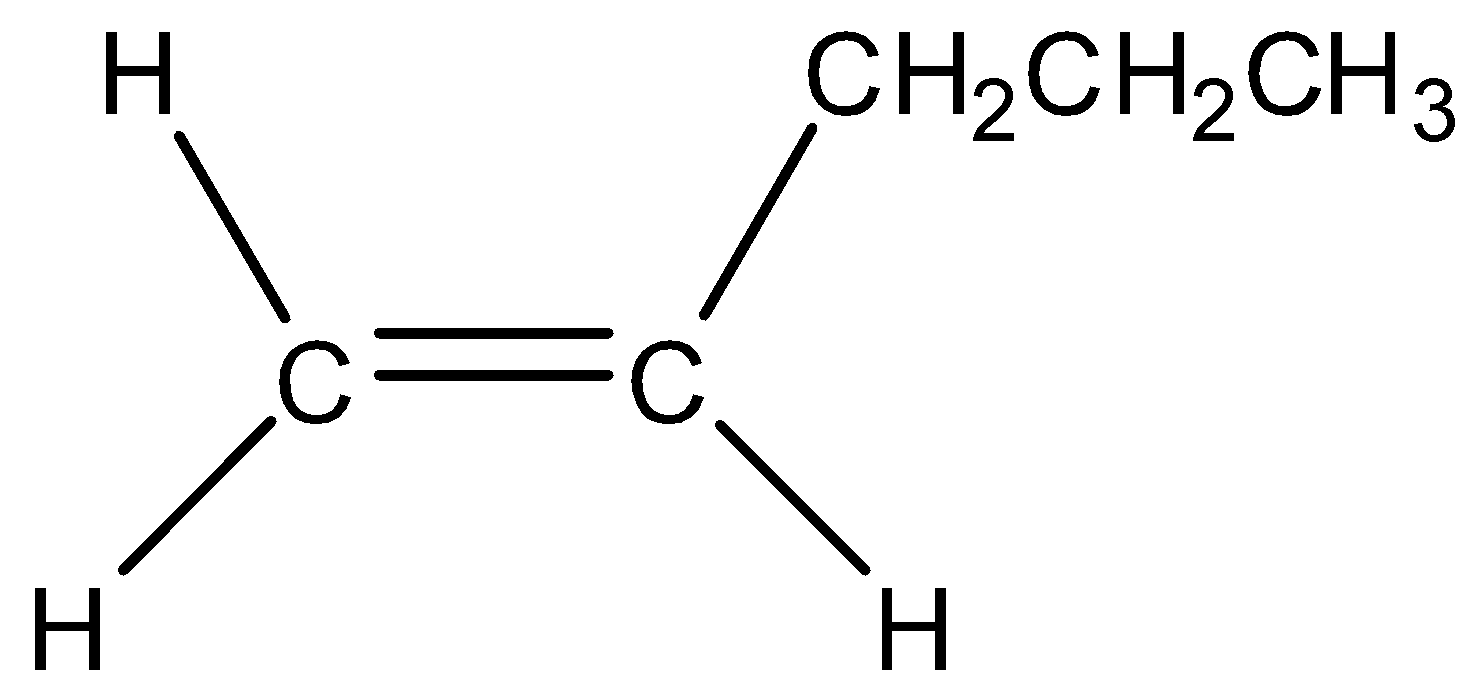
A disubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms bond to two other carbon atoms. Now we draw the disubstituted alkene of C5H10.
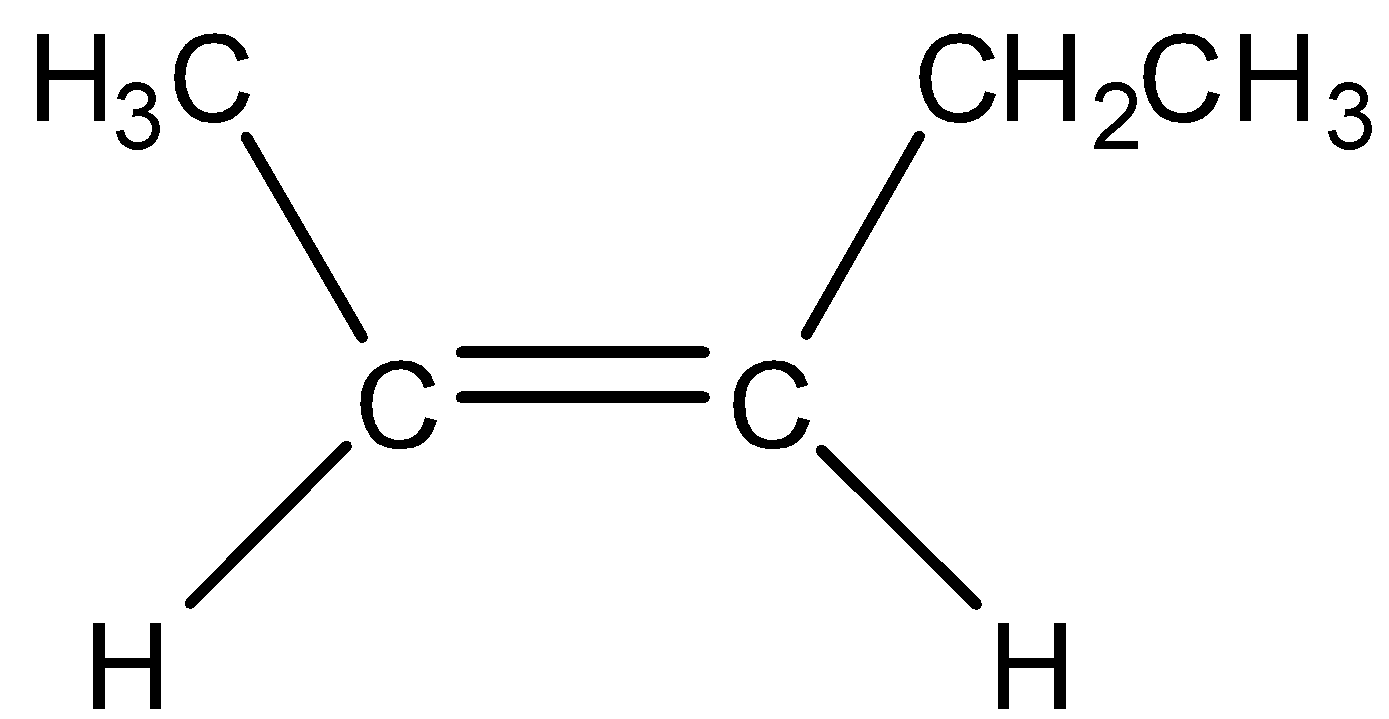
A trisubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms bonded to three carbon atoms. Now we draw the trisubstituted alkene of C5H10.
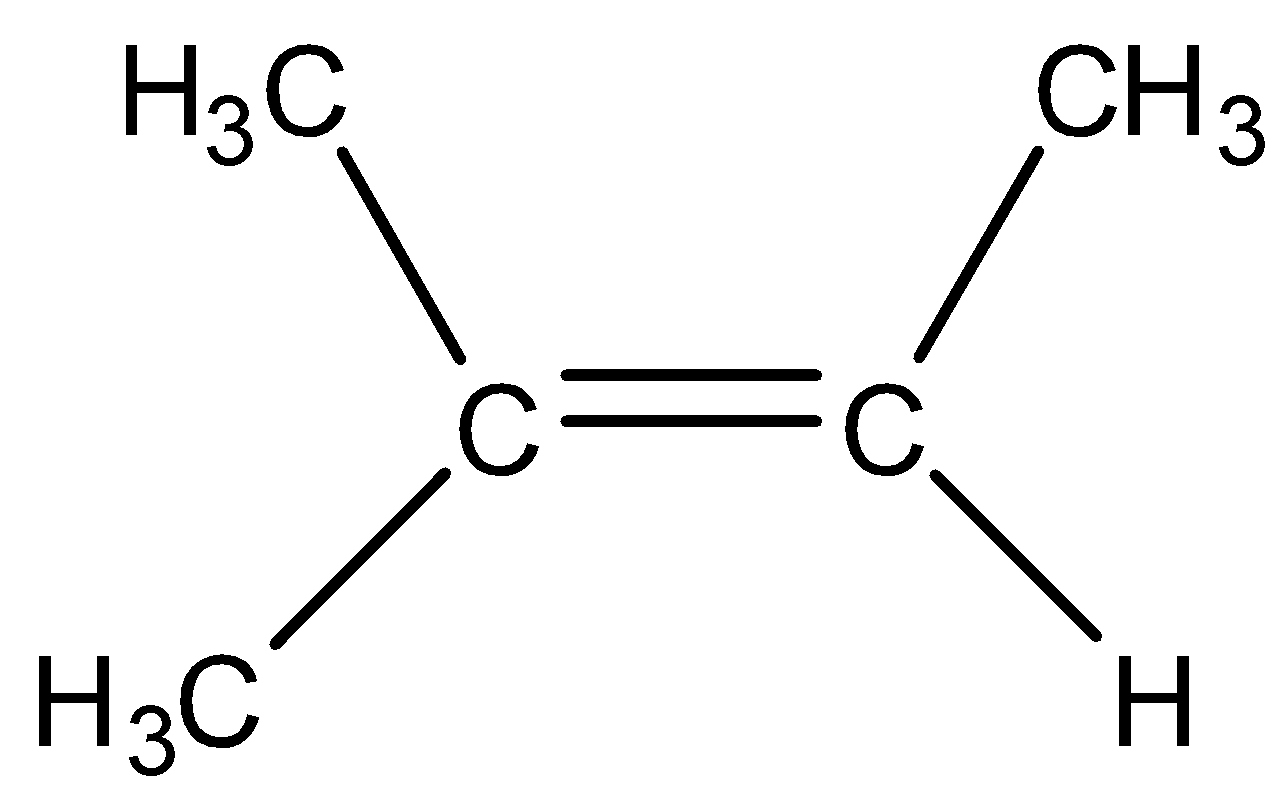
A tetrasubstituted alkene is the alkene in which double bonded carbon atoms bonded to three other carbon atoms. For C5H10, formation tetrasubstituted alkene is not possible because minimum six carbon atoms are required for its formation, that is, two at the C=C bond and four carbon atoms which is to be substituted. But in C5H10, only five carbon atoms are present.
So, we can say that, C5H10 forms monosubstituted, disubstituted and tetrasubstituted alkene but it cannot form tetrasubstituted alkene.
Hence, option A, B and C is correct.
Note: Isomers are compounds which possess the same molecular formula but they have different structures. Monosubstituted, disubstituted and trisubstituted alkene of C5H10 are isomers of each other because they have same number of hydrogen and carbon atoms but their structures are different.
