Question
Question: A hydrocarbon has a molecular formula\[{{\rm{C}}_6}{H_8}\] and it can be resolved into enantiomers. ...
A hydrocarbon has a molecular formulaC6H8 and it can be resolved into enantiomers. However, catalytic hydrogenation of the above hydrocarbon gives 3−methyl pentane. Deduce the structure of hydrocarbon.
Solution
As we know that, the hydrocarbons are those which are having carbon and hydrogen in its composition, the bonding between hydrocarbons can be single, double or triple bonding such as alkanes are bonded with single bonding (CnH2n+2) , alkene are bonded with double bonding(CnH2n)and alkyne are bonded with triple bonding(CnH2n−2).
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrocarbons contain hydrogen and carbon with multiple bonding. There are mainly three types of hydrocarbons.
Alkane are hydrocarbon which is bonded with single bonding and represented as CnH2n+2.
Alkene are hydrocarbon which is bonded with double bonding and represented as CnH2n.
Alkynes are hydrocarbon which is bonded with triple bonding and represented asCnH2n−2.
Now, the above given formula is C6H8. So, this does not belong to the above particular hydrocarbon. It also can be resolved into enantiomers meaning it has chiral carbon which is optically active. The compound should be shown as
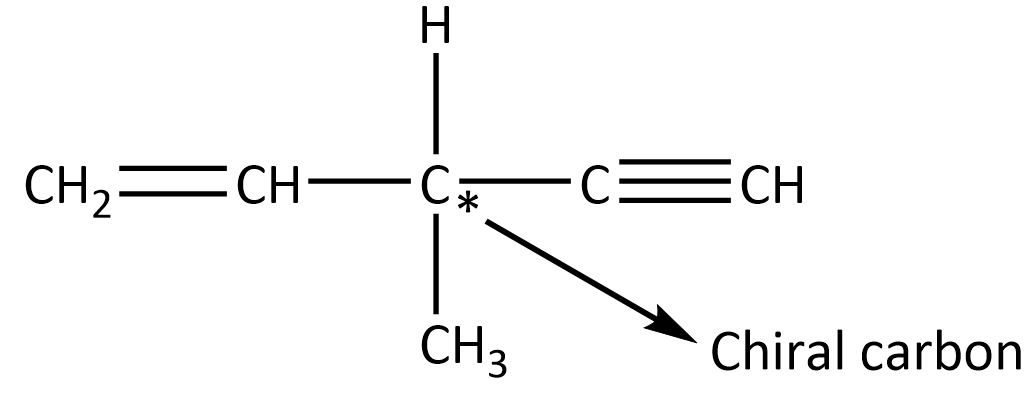
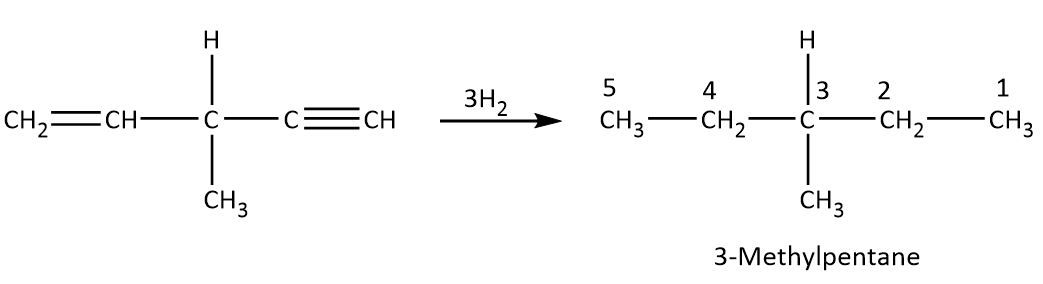
Now this compound when we treat with three moles of hydrogen in the presence of Raney nickel, the hydrogen reduces the double bond by its one mole and other two moles of hydrogen is involved to reduce triple bond then finally we get final product 3−methyl pentane, as shown below.
Note:
The enantiomers are of two type-
(a) Resolved enantiomers in which a particular configuration (either Ror S )is more in yield.
(b) Racemic mixture- the enantiomers are equal in ratio.
